Company Training Academy for Consultants
Deliver powerful cybersecurity training to your clients – effortlessly
Learning management system designed specifically for consultants that want to offer online training for their clients. With a single dashboard, you can onboard clients, manage their training accounts, monitor progress, and grow your business through white-label compliance training solutions.
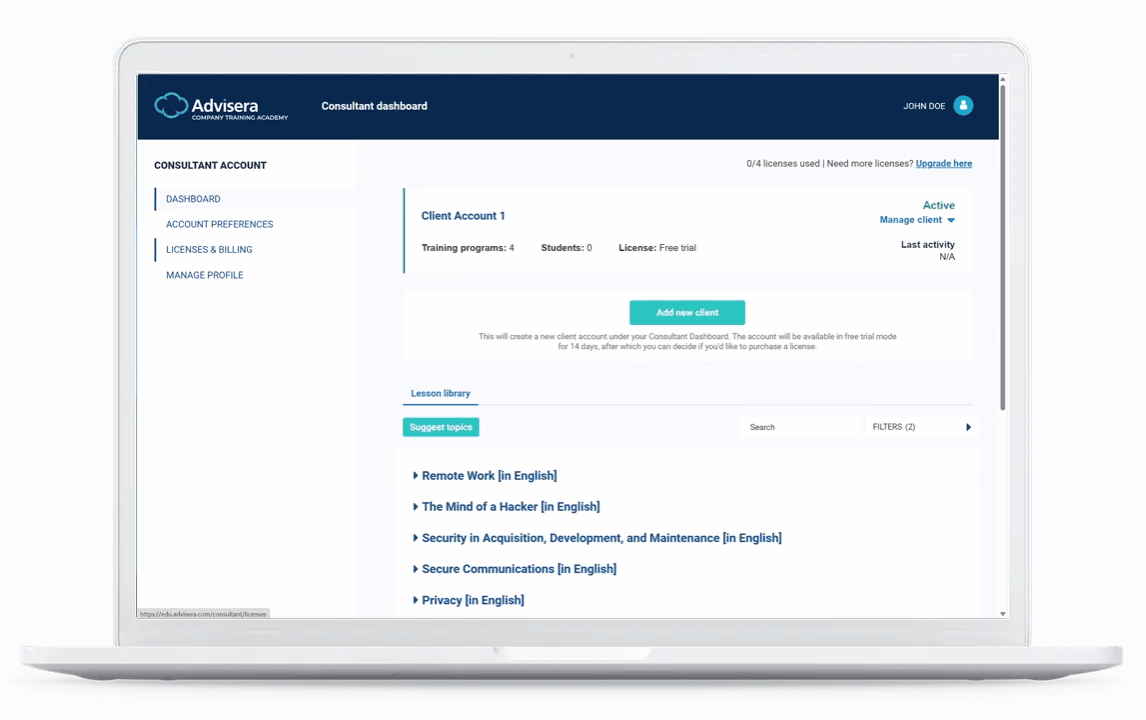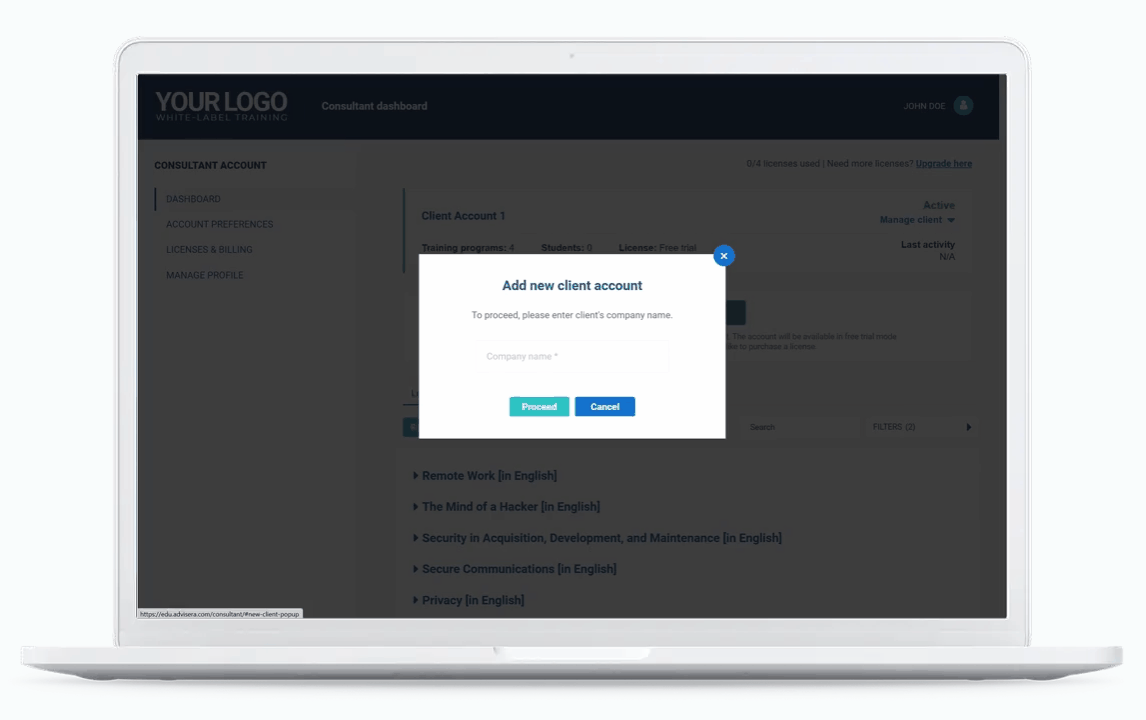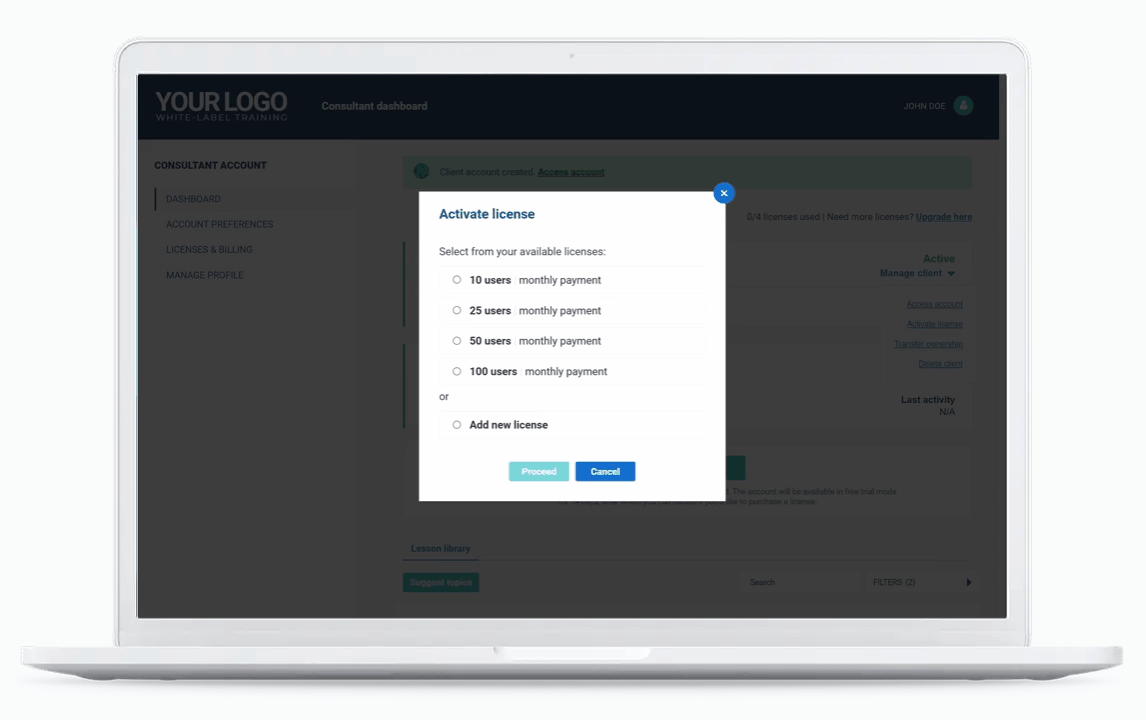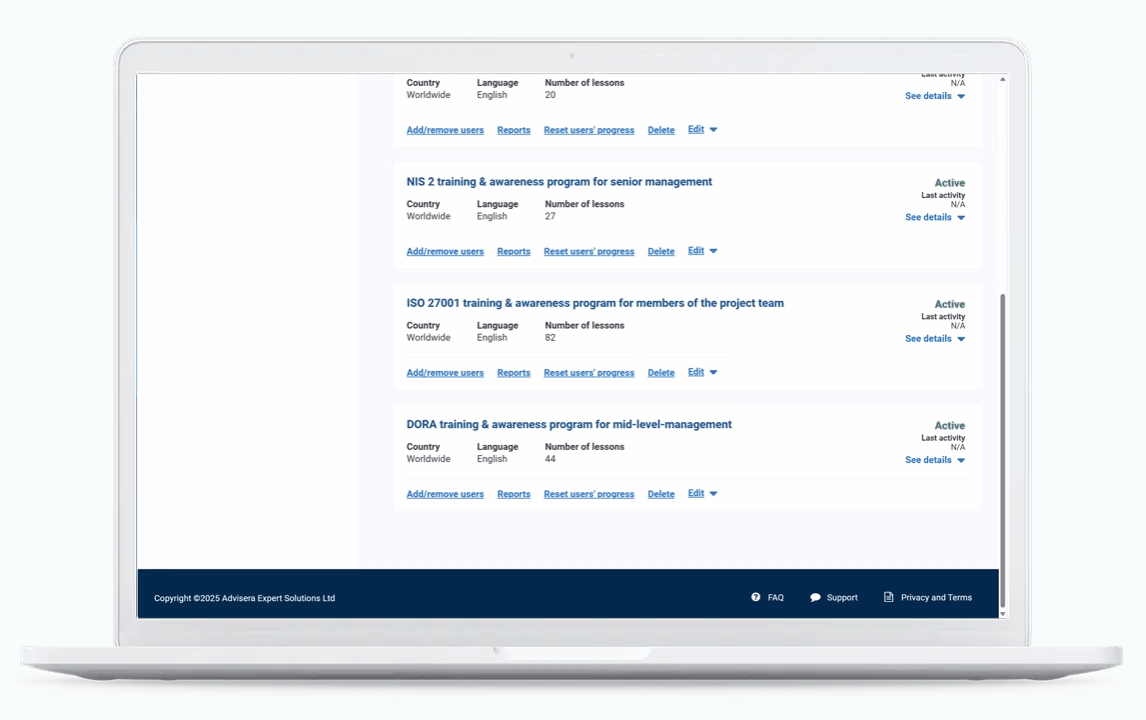
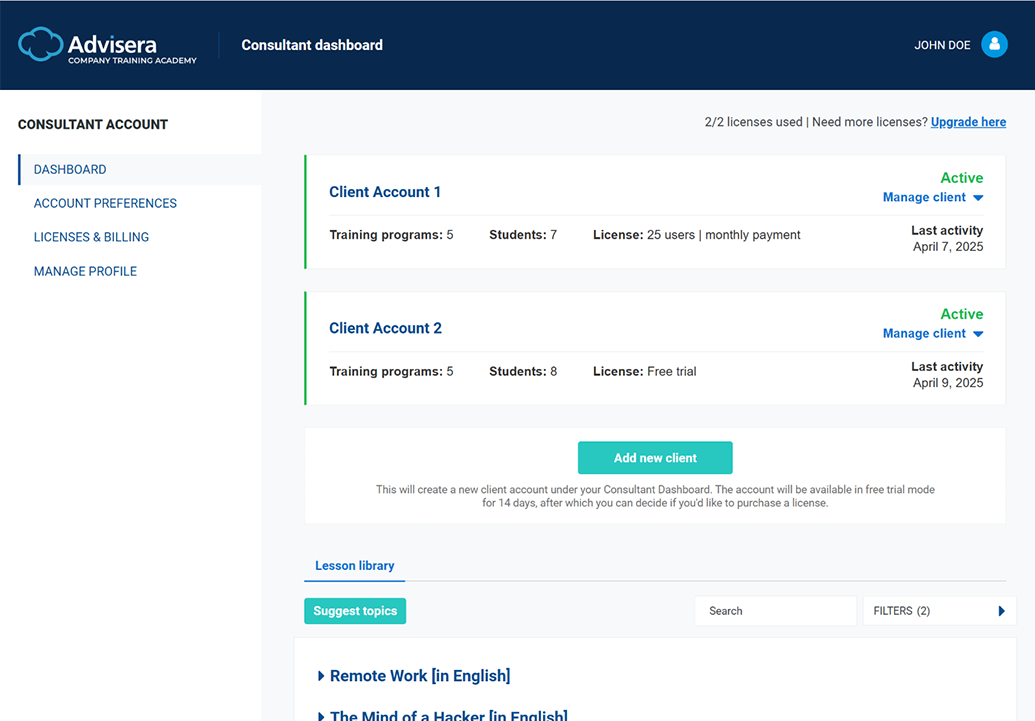
Built for consultants managing multiple clients
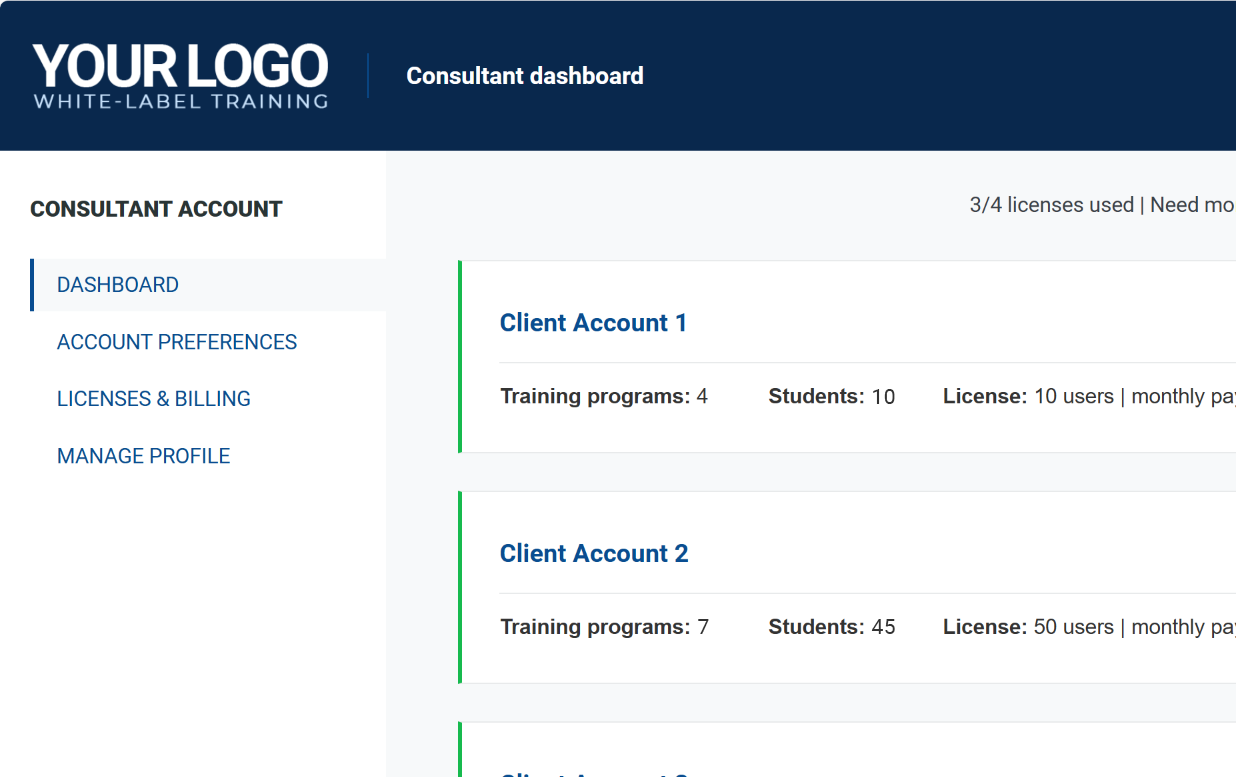
With the new multi-account management system, you can open and manage separate training accounts for each of your clients – from a single interface.
- Manage all clients from one dashboard.
- Create, monitor, and customize separate training programs.
- Delegate access to training administrators, or manage everything yourself.
Biggest library of cybersecurity videos
Each client has different compliance needs — we help you meet them. Our library of 400+ short, expert-led training videos cover the following topics:
- NIS2
- DORA
- ISO 27001
- GDPR
- ISO 42001
- Security awareness
Lessons library
- What is NIS2? (6:27)
The basics of EU cybersecurity directive
- Basic Cyber Hygiene Practices (4:47)
Essential cybersecurity measures for every user
- Handling Cybersecurity Incidents (6:16)
How to spot and react promptly to cybersecurity concerns
- Disaster Recovery (8:38)
How to recover information systems and data
- Cryptography (10:39)
Cryptographic concepts and their application
- Access Control (6:07)
Permitting appropriate access and preventing inappropriate access
- Cyber Asset Management (7:22)
Identifying, classifying, securing, and exploiting digital assets
- Basics of Network Security (6:43)
Securing digital networks and data communications
- NIS 2 Certification and Standardization (7:52)
Explanation of NIS 2 articles 24 and 25
- NIS 2 Supply Chain Security (9:16)
Management of cyber risks related to suppliers
- Backup basics (4:36)
Recovery from data loss
- Business Continuity (9:40)
Resilience and recovery arrangements
- Basics of Authentication (6:05)
Preventing unauthorized access to digital assets
- NIS 2 Policy on Information System Security (10:01)
Writing a top-level cybersecurity policy for NIS 2
- Security in Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance (12:15)
Cybersecurity in the IT system lifecycle
- Emergency Communications (6:30)
Setting up alternative communication methods
- NIS 2 Authorities (6:31)
8 government bodies in charge of enforcing NIS 2
- Cybersecurity Training and Awareness (11:33)
Creating a program for continuous training and awareness
- Human Resources Security (12:57)
Activities before, during, and after employment
- Measuring Cybersecurity (7:59)
Assessing the effectiveness of risk management
- Corrective Actions (8:02)
How to eliminate the cause of nonconformities
- NIS 2 Applicability (6:26)
Essential and important organizations that must be compliant
- NIS 2 Cybersecurity Requirements (8:51)
10 most important NIS 2 cybersecurity measures
- Management’s Role in Cybersecurity (7:34)
Tasks for senior and mid-level management
- NIS 2 Incident and Crisis Management (10:28)
Management of cyber risks related to suppliers
- NIS 2 Reporting Obligations (8:49)
How to disclose significant incidents
- NIS 2 Enforcement (10:19)
Key actions authorities can use to enforce compliance
- Secure Communications (13:32)
Securing voice, video, and text communication channels
- Insider Threats (6:30)
Managing insiders with access to sensitive information
- Cloud Security Basics (5:38)
Securing data when using cloud services
- NIS 2 Implementation Steps (7:23)
15 steps to achieve full cybersecurity compliance with NIS 2
- Assessing Supplier Security (12:46)
Supplier vulnerabilities, quality, and secure development
- Computer Malware (4:58)
Phishing, ransomware, and spyware
- Email Security (4:08)
Risks related to the usage of email
- Human Error (4:33)
Reducing mistakes with sensitive information
- Identity Theft (4:58)
How do cybercriminals steal your identity?
- The Mind of a Hacker (5:42)
3 types of hackers and how to protect yourself
- Information Risk Management (8:29)
Risk assessment and treatment as a foundation of cybersecurity
- Passwords (5:30)
Creating and keeping passwords secure
- Device Physical Security (5:52)
Physically securing information and devices
- Privacy (4:36)
8 privacy principles everyone should know
- Intellectual Property (5:36)
Technical, legal, and organizational methods of protecting IPR
- Protecting Paperwork (6:35)
Vulnerabilities of paper media, and methods of protecting it
- Security of Mobile Devices (5:30)
Protecting laptops, tablets, smartphones, and other devices
- Social Engineering (6:02)
The most common methods criminals are using to access your account
- Social Media (5:24)
Main cyber risks when using Facebook, X, LinkedIn, and others
- Remote Work (4:37)
Risks when working outside of office premises
- Managing Supplier Security (6:32)
Risks related to vendors and contractors, and how to handle them
- Croatia’s Cybersecurity Act (5:57)
Similarities and differences with NIS 2
- What is ISO 27001? (1:02)
Learn about the basics of the leading cybersecurity standard
- The structure of ISO 27001 (2:01)
ISO 27001 main clauses and their purpose
- Information security principles used in ISO 27001 (2:07)
An example of confidentiality, integrity, and availability in practice
- ISO 27001: Introduction to the ISMS (2:22)
The purpose of an Information Security Management System
- Key roles in ISO 27001 implementation (1:07)
Roles of the project manager, security officer, and senior management
- Documenting ISO 27001 requirements (2:55)
Mandatory and non-mandatory documents
- Implementing ISO 27001 requirements (2:13)
Using the PDCA cycle as guidance for implementation
- ISO 27001 Benefits (2:02)
4 key benefits: compliance, marketing, costs, and better organization
- ISO 27001: Understanding your organization and its context (2:03)
Analyzing internal and external issues
- ISO 27001: Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties (1:35)
Who are interested parties, and what are their requirements?
- ISO 27001: Determining the scope of the ISMS (1:50)
What is the ISMS scope, and why is it important?
- ISO 27001: Leadership and commitment (1:45)
Key senior management activities that represent commitment
- ISO 27001: Information Security Policy (1:13)
Mandatory elements of this top-level policy
- ISO 27001: Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities (2:14)
Which roles are mandatory according to ISO 27001?
- ISO 27001: Information security objectives (2:14)
Why are objectives important, and how to define them?
- ISO 27001: Resources (1:40)
Example of resources and how to document them
- ISO 27001: Competence (1:22)
The options to acquire required skills and knowledge
- ISO 27001: Awareness (1:23)
How to organize security awareness in a company
- ISO 27001: Communication (1:24)
What kind of communication is required, and why is it important?
- ISO 27001: Documented information (3:12)
Creating, updating, and controlling policies, procedures, and records
- ISO 27001: Addressing risks and opportunities (1:46)
The basics of risk management
- ISO 27001: Risk management process (2:15)
Five key steps to assess and treat risks
- ISO 27001: Information security risk assessment – Risk identification (3:03)
Risk identification, risk analysis, and risk evaluation
- ISO 27001: Information security risk assessment – Risk analysis and evaluation (2:40)
Using scales to assess impact and likelihood
- ISO 27001: Information security risk treatment (0:00)
Four most common options for treating risks
- ISO 27001: Statement of Applicability (1:59)
The purpose and structure of the SoA
- ISO 27001: Formulating the risk treatment plan (1:49)
The purpose and mandatory elements of the RTP
- ISO 27001: Implementing the risk treatment plan (1:15)
Key elements of implementation and how to document results
- ISO 27001: Operational planning and control (2:18)
Key elements of the Do phase in the PDCA cycle
- ISO 27001: Operating the ISMS (1:18)
What does operating the ISMS mean?
- ISO 27001: Managing outsourcing of operations (1:57)
Examples of security controls for outsourcing activities
- ISO 27001: Controlling changes (1:58)
An example of a change management procedure
- ISO 27001: Risk assessment review (1:46)
Why is risk review important, and how often to perform it?
- ISO 27001: Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation (3:13)
Key elements for evaluating the performance of the ISMS
- ISO 27001: Internal audit (2:35)
Key elements of an internal audit
- ISO 27001: Management review (2:30)
Inputs and outputs for the management review meeting
- ISO 27001: Nonconformities and corrective actions (3:22)
Required actions when a nonconformity occurs
- ISO 27001: Continual improvement (2:19)
Examples of improvement initiatives
- ISO 27001: Introduction to Annex A (5:18)
The purpose and structure of Annex A
- ISO 27001: People controls (2:05)
Overview of Annex A.6 – Controls before, during, and after employment
- ISO 27001: Physical controls (3:37)
Overview of Annex A.7 – Securing physical areas and equipment
- ISO 27001: Technological controls – overview and new controls (4:13)
Overview of Annex A section A.8 – Technological controls
- ISO 27001: Technological controls – software development (2:51)
Controls that cover architecture, lifecycle, testing, and coding principles
- ISO 27001: Organizational controls – operational security (2:43)
Controls for access control, information transfer, operating procedures, etc.
- ISO 27001: Organizational controls – policies and responsibilities (3:22)
Controls for roles, segregation of duties, contact with external parties, etc.
- ISO 27001: Organizational controls – information and asset management (1:52)
Controls for asset inventory, acceptable use, classification, etc.
- ISO 27001: Technological controls – operational security (4:48)
Controls that cover security in day-to-day IT activities
- ISO 27001: Organizational controls – supplier security (3:14)
Controls for assessing risks, contractual requirements, monitoring, etc.
- ISO 27001: Organizational controls – incidents and business continuity (4:52)
Controls to deal with threats, events, incidents, and larger disruptions
- ISO 27001: Organizational controls - compliance, privacy, and legal aspects of security (2:49)
Controls that ensure security is compliant with legal requirements
- What is DORA? (3:46)
EU regulation for digital resilience in financial sector
- Who needs to comply with DORA? (2:41)
Which financial institutions and other companies must comply?
- Which IT providers need to comply with DORA and how? (3:49)
Securing ICT Supply Chains for Financial Resilience
- What are DORA-related regulations? RTS, CDR, and CIR (3:13)
Additional Requirements Through Regulatory Technical Standards
- What are the main requirements specified in DORA? (3:45)
Summary of 9 Most Important Requirements
- DORA implementation steps (4:54)
Optimal Steps for DORA Compliance Project Implementation
- Writing DORA documentation (3:30)
Structure and Content of DORA Documentation
- DORA: Organizing training and awareness (2:57)
Key training & awareness requirements and how to comply with them
- DORA: Penalties and fines (3:08)
Who Enforces Them and How Do They Look Like?
- DORA: Governance responsibilities for senior management (2:30)
Implementing Internal Governance & ICT Risk Oversight
- DORA: Key elements of ICT risk management framework (3:42)
Description of Overall Activities in ICT Risk Management Framework
- DORA: Developing top-level information security policy (1:54)
Content of the Top-level Policy
- DORA: How to write Digital operational resilience strategy (3:06)
Key Elements of the Strategy
- DORA: Identifying ICT-supported business functions and assets (1:36)
ICT Function Mapping & Asset Lifecycle Management
- DORA: Performing risk assessment (2:43)
Mandatory Elements of ICT Risk Assessment
- DORA: Learning and evolving (2:40)
Methods for Continuous Cybersecurity Evolution
- DORA: Measurement, monitoring, and controlling the ICT systems (1:14)
Elements of Continuous Measurement, Monitoring, and Controlling
- DORA: Internal audit of ICT risk management framework (1:23)
Performing Internal Audit for ICT Risk Compliance
- DORA: Follow-up and corrective actions (2:16)
The Purpose and Content of the Follow-up
- DORA: Report on the review of ICT risk management framework (2:23)
Details of the Annual Review and Reporting
- DORA: Main elements of simplified ICT risk management framework (6:42)
Requirements for Small Financial Entities
- DORA: Policies and procedures for ICT operations security (1:40)
The Content of Operational Security Documents
- DORA: Capacity and performance management (1:39)
Optimizing ICT Capacity and Performance for Operational Resilience
- DORA: Data and system security (2:12)
Comprehensive Data and System Security Procedure Requirements
- DORA: Network security management (1:58)
Main Methods for Ensuring Network Security
- DORA: Securing information in transit (1:39)
Ensuring Secure Data Transmission and Confidentiality
- DORA: Encryption and cryptography (2:02)
Management of Encryption and Cryptographic Keys
- DORA: Human resources policy (1:31)
HR's Role in Digital Operational Resilience
- DORA: Identity management and authentication (1:13)
Requirements for Identity Policies and Authentication Mechanisms
- DORA: Access control (2:38)
Regulatory Requirements and Best Practices for Access Control
- DORA: Physical and environmental security (1:36)
Physical and Environmental Security Policy for ICT Assets
- DORA: ICT systems acquisition, development, and maintenance (2:36)
ICT Systems Lifecycle Security Policy and Testing
- DORA: ICT project management (1:24)
Rules for Managing ICT Projects
- DORA: ICT change management (2:16)
Elements of Change Management for Secure ICT Systems
- DORA: Logging (1:14)
Logging Procedures for Recording Critical Events
- DORA: Detecting anomalous activities (1:40)
Elements of Collecting and Analyzing Activities
- DORA: Vulnerabilities, patch management, and updates (2:11)
Vulnerability Management and Patch Processes for ICT Systems
- DORA: Incident management process (2:51)
Systematic Incident Handling and Rapid Response
- DORA: Classification of ICT incidents and threats (4:05)
Detailed Classification Criteria
- DORA: Reporting major incidents and cyber threats (3:05)
Types of Incident Reports for Authorities
- DORA: ICT business continuity policy (2:13)
Elements of the Top-level Business Continuity Document
- DORA: Business impact analysis, RTO, and RPO (1:44)
The Purpose of RTOs and RPOs for Business Continuity
- DORA: Backup and restoration of data (2:01)
Detailed Rules for Setting Up Backup and Restoration
- DORA: Secondary processing site (1:36)
Alternative Site Requirements for Central Counterparties
- DORA: ICT response and recovery plans (2:02)
Requirements for the Content of the Plans
- DORA: Testing business continuity and recovery plans (3:03)
Detailed Requirements for Plan Testing
- DORA: Crisis management and communication (1:33)
Elements of Handling Crisis
- DORA: Main elements of digital operational resilience testing (2:07)
Comprehensive Testing Program for ICT Risk Resilience
- DORA: Resilience testing of ICT tools and systems (1:31)
Types of Resilience Tests
- DORA: Threat-Led Penetration Testing TLPT (3:15)
Requirements for TLPT and for Testers
- DORA: Key elements ICT third-party risk management (4:30)
Governance, Assessment, Contracts, and Exit Strategies
- DORA: Selecting critical ICT service providers (3:29)
Critical ICT Provider Designation and Oversight Framework
- DORA: Risk assessment of ICT service providers (3:02)
Assessing Suppliers Before Signing Contracts
- DORA: Contracts with ICT service providers (4:32)
Standardized Security Clauses for Protection of ICT Services
- DORA: Register of information (3:43)
Standardized Register for ICT Contractual Oversight
- DORA: Monitoring, inspection, and audit of ICT service providers (2:17)
Independent Review and Ongoing Monitoring
- DORA: Exit strategies for ICT services (3:48)
Enabling a Smooth Transition Away From a Service Provider
- DORA: Government oversight of critical ICT service providers (2:56)
The Tasks and Powers of the Lead Overseer
- What is EU GDPR and where does it apply? (1:35)
EU GDPR: Protecting data rights and setting global standards for personal data processing.
- Which frameworks are related to GDPR? (1:33)
Leveraging ISO standards (27701, 27001, 29100) and OECD guidelines to reinforce GDPR best practices.
- Key terms in GDPR (6:34)
Essential GDPR vocabulary covering personal data, processing, roles, and data protection techniques.
- Key roles according to GDPR (2:07)
Key GDPR roles: Controllers, processors, DPOs, and supervisory authorities shape compliance responsibilities.
- Business activities that are impacted the most by GDPR (1:53)
Discover how GDPR affects diverse business functions, from Marketing and IT to HR and beyond.
- Six legitimate purposes of processing personal data according to GDPR (3:58)
Six legitimate processing purposes under GDPR: from contracts to consent
- What are the main GDPR principles? (2:58)
GDPR principles: lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, minimisation, accuracy, security, and storage limits.
- Real-world example for understanding main GDPR principles (4:10)
How GDPR’s principles—transparency, minimisation, consent, and timely deletion—apply in practice.
- The basics of Privacy Notices according to GDPR (2:31)
Clear disclosures on data processing to ensure transparency under GDPR.
- Contents of a Privacy Notice according to GDPR (2:04)
Clear, plain disclosures on data collection, processing, rights, contacts, and safeguards
- What is GDPR Inventory of Processing Activities (4:58)
How to build and maintain an Inventory of Processing Activities to meet GDPR requirements.
- What is GDPR personal data retention (2:05)
What does data retention mean, and how to ensure compliance with GDPR requirements.
- Responsibilities for fulfilling GDPR requirements for inventory and retention (3:01)
How to define clear roles and processes for maintaining GDPR inventories and retention schedules.
- The content of GDPR Inventory of Processing Activities for controllers (1:19)
Inventory for controllers: DPO, processing purposes, data categories, recipients, transfers, retention limits, and safeguards.
- The content of GDPR Inventory of Processing Activities for processors (1:17)
Essential details on sub-processors, controllers, processing categories, and data transfers.
- GDPR Consent – The basics (2:42)
What is GDPR consent is, and what its key requirements are?
- How and when to ask for GDPR consent (1:49)
Learn how and when to request consent under GDPR, ensuring transparency and user choice.
- Data subject rights according to GDPR (3:24)
Learn how data subject rights empower individuals to control their personal data under GDPR.
- Basic GDPR rules for data subject access rights (2:01)
DSAR basics, from valid request formats to response timelines.
- Handling DSAR requests according to GDPR (1:20)
DSAR best practices, response timelines, and identity verifications under GDPR.
- DSAR exemptions and rejections according to GDPR (2:31)
How to handle DSAR queries, typical exemptions, and valid grounds for rejections.
- What is Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) according to GDPR? (2:05)
How DPIAs help identify and mitigate risks in data processing.
- DPIA Step 1 according to GDPR: Listing and grouping data processing activities (1:04)
How to identify and group data processes for assessment.
- DPIA Steps 2 and 3 according to GDPR: The threshold questionnaire & determining if DPIA is needed (1:45)
How high-risk processing is identified accurately with a threshold questionnaire.
- DPIA Steps 4, 5 and 6 according to GDPR: Answer the DPIA questionnaire, identify and list key security risks (2:40)
What is needed for DPIA steps and how to address key security risks
- Step 7 DPIA according to GDPR: Recording the implementation; maintenance (1:02)
Regular DPIA reviews keep safeguards updated and documented for compliance.
- What is Data Protection by Design and by Default according to GDPR? (2:00)
Data Protection by design and by Default concepts for building data protection into processes and systems
- GDPR policies to be implemented to ensure security of personal data (5:26)
Key policies that support secure data practices and mitigate privacy risks.
- Best practices to implement GDPR Data Protection by Design and by Default policies (2:16)
Key steps for defining and maintaining GDPR Data Protection by Design and by Default policies.
- Introduction to GDPR data transfers (2:06)
Managing personal data transfers, adequacy measures, and GDPR compliance.
- How can GDPR data transfers be enabled? (2:55)
How to choose suitable mechanisms for lawful international data transfers
- Managing third parties according to GDPR (1:57)
How to ensure GDPR compliance when engaging third-party processors and service providers
- GDPR basic rules for data breaches (3:40)
When personal data is exposed or stolen: rules for compliance and best practices.
- Data breach response according to GDPR (1:14)
Swift actions and logging procedures to address data breaches.
- GDPR data breach notifications (1:29)
Essential guidelines for data breach notifications under GDPR.
- What to do after a data breach according to GDPR (1:04)
How to evaluate data breaches, contain damage, and prevent future risks.
- Why does a company need a DPO? (2:18)
Key details about the DPO’s role, appointment, and responsibilities.
- The responsibilities of the DPO (4:16)
Detailed obligations, tasks, and best practices for a DPO under GDPR
- Responsibilities towards the DPO (1:09)
Ensuring DPO independence, resources, and timely involvement.
- Define a GDPR Personal Data Protection Policy (3:57)
How to define a personal data protection policy for clear GDPR alignment.
- Setting up privacy governance for GDPR (1:36)
Arranging departmental champions, boards, and consistent reviews for privacy compliance
- Key steps in your GDPR project (2:55)
Key steps to launch or refine GDPR compliance within an organization.
- Conducting a GDPR Gap Analysis (2:47)
Identify, assess, and address key GDPR requirements through a gap analysis.
- GDPR Awareness and Training (4:38)
How to plan effective GDPR awareness and training across teams and tasks.
- Methods for sustaining and improving GDPR compliance (1:34)
How to sustain and improve GDPR compliance in a changing environment.
- Handling existing contracts with third parties to comply with GDPR (3:00)
How to align third-party agreements with GDPR requirements.
- Handling new contracts with third parties according to GDPR (3:30)
Ensuring robust selection, contractual terms, and ongoing reviews under GDPR.
- Regular GDPR reviews and improvement actions (2:41)
Regular checks on DPIAs, DSAR handling, and staff training to keep compliance alive.
- What is ISO 42001? (1:21)
Overview of the ISO 42001 standard for AI governance
- The structure of ISO 42001 (2:42)
Understand ISO 42001 clauses and annexes for building an effective AIMS
- ISO 42001: General objectives for AI (2:14)
Learn ISO 42001 Annex C.2 objectives for accountable and fair AI governance
- ISO 42001: Introduction to the Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS) (2:18)
Explore the structure and purpose of AIMS for systematic AI governance
- Implementation of ISO 42001 according to PDCA cycle (1:18)
Apply the PDCA cycle to implement and improve an ISO 42001 AIMS
- Implementing ISO 42001 as a project (2:06)
Manage ISO 42001 implementation as a structured compliance project
- ISO 42001: Documenting the AIMS (3:59)
Learn ISO 42001 documentation requirements for AI governance and controls
- Benefits of ISO 42001 (1:48)
Discover organizational, compliance, and ethical benefits of ISO 42001 adoption
- ISO 42001: Related standards and regulations (2:28)
See how ISO 42001 aligns with ISO 22989, 23894, 42005 and the EU AI Act
- ISO 42001: Explanation of basic AI terminology (3:25)
Understand ISO 22989 AI concepts and terminology that are important for AI governance
- ISO 42001: Understanding machine learning and its main types (3:19)
Explore ISO 22989 machine learning types relevant to AI governance
- ISO 42001: Understanding neural networks and their types (3:04)
Learn how ISO 22989 defines neural network types essential for AI system design
- ISO 42001: Main components of an AI system (1:38)
Learn what are the functional components of AI systems per ISO 22989
- ISO 42001: AI system life cycle (3:56)
Understand AI system life cycle stages aligned with ISO 42001 requirements
- ISO 42001: Understanding the organization and its context (2:34)
Define AI roles, internal and external issues to set the context for your AIMS
- ISO 42001: Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties (1:33)
Identify stakeholders and their AI governance expectations under ISO 42001
- ISO 42001: Determining the scope of the AIMS (1:24)
Establish and document the boundaries of your AIMS per ISO 42001
- ISO 42001: AI management system (1:47)
Learn to structure and operate an AIMS aligned with ISO 42001 clauses
- ISO 42001: Leadership and commitment (1:28)
Ensure senior management commitment for effective AIMS implementation
- ISO 42001: AI policy (2:44)
Develop and maintain a documented AI policy with elements required by ISO 42001
- ISO 42001: Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities (2:46)
Define and communicate AI governance roles and responsibilities
- ISO 42001: Resources (1:44)
Identify and document resources required to operate the AIMS
- ISO 42001: Competence (1:40)
Establish competence requirements and training for AI governance roles
- ISO 42001: Awareness (1:26)
Promote awareness of AI governance and AI responsibilities across the organization
- ISO 42001: Communication (1:29)
Define AI-related internal and external communication requirements
- ISO 42001: Documented information (3:33)
Control AIMS documents and records per ISO 42001 requirements
- ISO 42001: Addressing risks and opportunities (1:39)
Identify AI risks and opportunities to enhance AIMS effectiveness
- ISO 42001: AI risk management process (3:24)
Establish a structured AI risk assessment and treatment process
- ISO 42001: Defining an AI risk management methodology (3:25)
Create a documented method for consistent AI risk management
- ISO 42001: AI risk identification (04:02)
How to identify AI risks and document them
- ISO 42001: AI risk analysis and evaluation (2:30)
Using scales for impact and likelihood and calculating the level of risk
- ISO 42001: AI risk treatment and Statement of applicability (3:18)
Mandatory elements of Risk treatment plan and Statement of applicability
- ISO 42001: AI system impact assessment (4:07)
Assess AI system impacts on individuals and society per ISO 42001
- ISO 42001: Setting AI objectives (2:42)
Define measurable AI objectives aligned with AI policy
- ISO 42001: Planning of changes (1:30)
Plan AI system changes to ensure controlled AIMS improvement
- ISO 42001: Operating the AIMS (1:51)
Integrating AIMS activities into everyday operations
- ISO 42001: Operational planning and control (3:25)
Implement processes and controls for effective AIMS operation
- ISO 42001: Implementing the AI risk assessment and treatment (2:37)
Apply and maintain AI risk assessment and risk treatment plans
- ISO 42001: Implementing the AI system impact assessment (1:42)
Conduct and review AI impact assessments regularly per ISO 42001
- Integration of ISO 42001 with ISO 27001, ISO 27701, and ISO 9001 (3:45)
Integrate AIMS with other ISO management systems for synergy
- ISO 42001: The basics of monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation (1:01)
Learn the difference and the purpose of performance management
- ISO 42001: Implementing monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation (2:51)
Techniques to implement effective AIMS performance measurement and reporting
- ISO 42001: Internal audit (3:00)
Plan and conduct AIMS internal audits to ensure ISO 42001 compliance
- ISO 42001: Management review (2:30)
How the senior management needs to participate in AIMS decision-making
- ISO 42001: Continual improvement (2:14)
Maintain continuous improvement of the AIMS per ISO 42001 principles
- ISO 42001: Nonconformities and corrective actions (3:41)
A systematic process of eliminating root causes of nonconformities
- ISO 42001: Purpose and structure of annexes A and B (4:48)
Understand the differences between Annexes A and B in AI control implementation
- ISO 42001: Policies related to AI (2:02)
Establish AI policies for responsible AI governance and review
- ISO 42001: Internal organization (1:30)
Define AI governance structure and responsible reporting processes
- ISO 42001: Resources for AI systems (2:52)
Identify and manage AI resources to support compliant AIMS operations
- ISO 42001: Assessing impacts of AI Systems (2:59)
Evaluate AI system impacts on individuals and society throughout lifecycle
- ISO 42001: Management guidance for AI system development (1:44)
Define responsible AI development objectives and processes
- ISO 42001: AI system life cycle (4:20)
Apply ISO 42001 controls across the AI system lifecycle stages
- ISO 42001: Data for AI systems (3:01)
Establish data management and quality controls for AI systems
- ISO 42001: Information for interested parties of AI systems (2:07)
Communicate AI system information and incident responses to stakeholders
- ISO 42001: Use of AI systems (2:37)
Ensure responsible and intended use of AI systems under AIMS
- ISO 42001: Third-party and customer relationships (1:51)
Manage third-party AI relationships to ensure accountability and compliance
White-label training for your brand
- You can apply your consultancy branding.
- Your clients will see only your brand when attending the training, not Advisera’s brand.
- You can choose whether to display your brand or your client’s brand in PDF reports.
Upload Your Own Training Materials
Add your consultancy’s or client’s materials to create fully tailored training for each customer. Upload documents, videos, policies, or presentations; then, turn them into clear lessons your clients’ employees can complete online — under your brand.

Thousands of Successful Customers
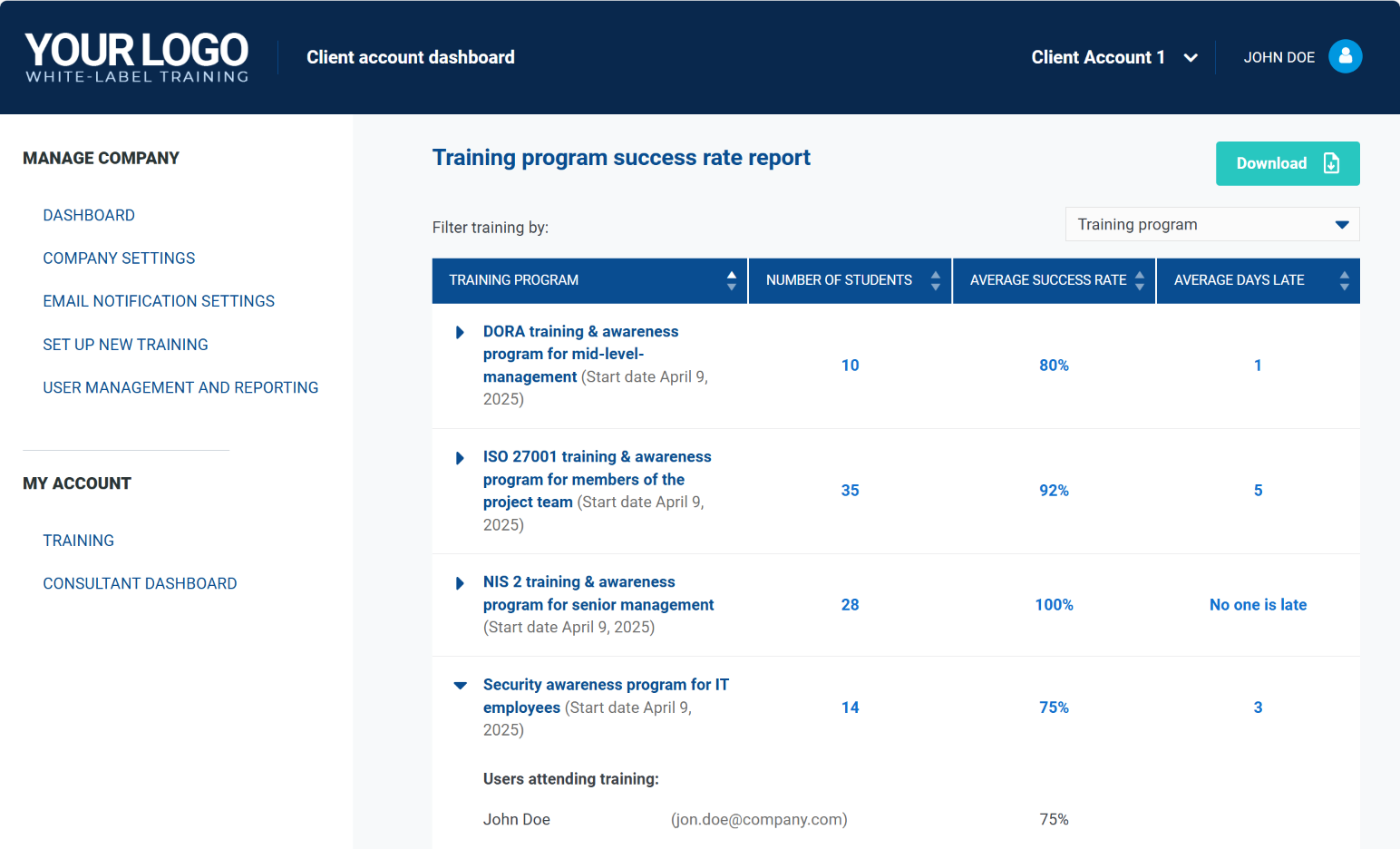
Automate training, reminders, and reporting
- Send training invitations to employees.
- Remind them about overdue lessons.
- Track progress and testing results.
- Generate audit-ready reports per client.
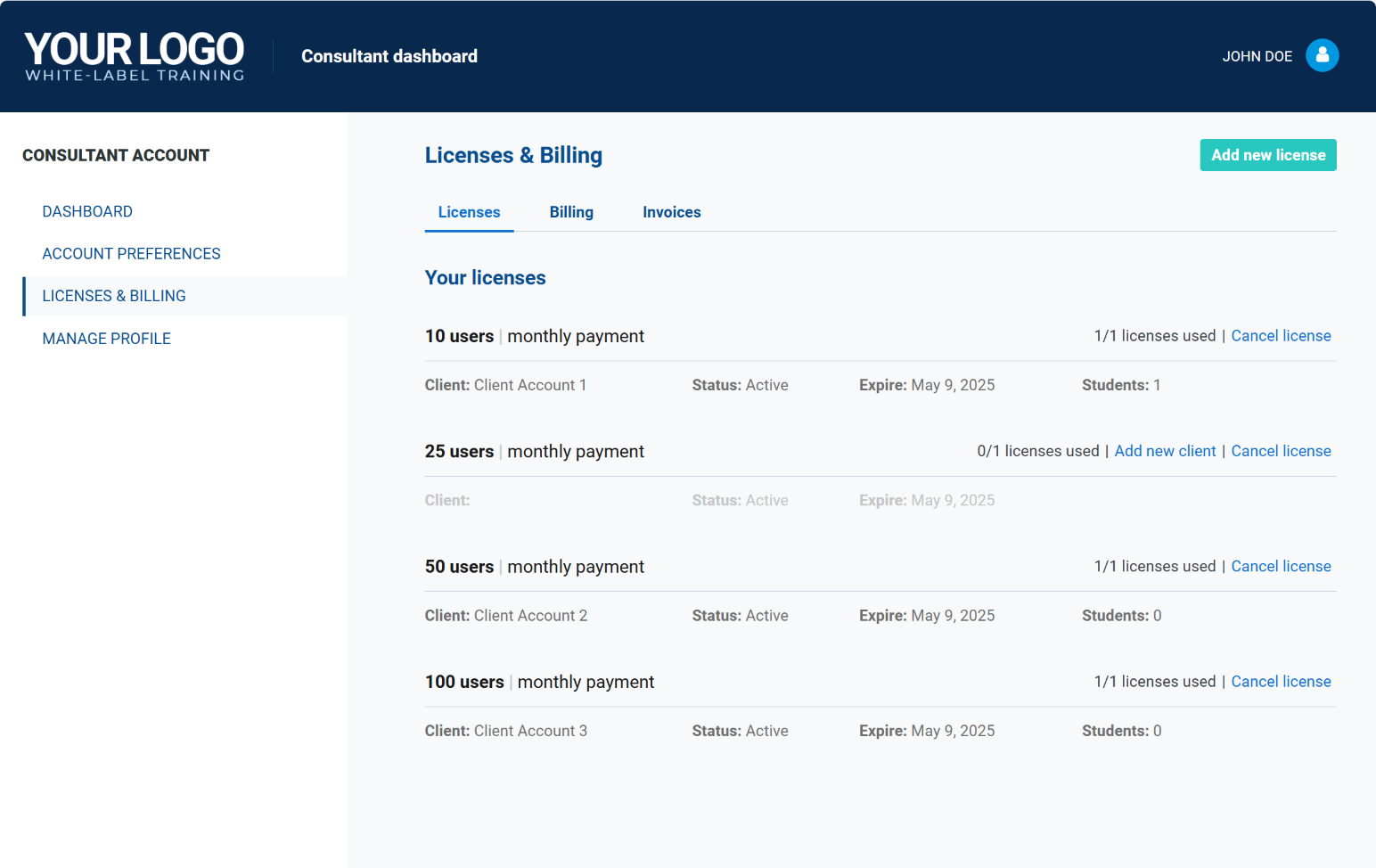
Make revenue from training services
- Add a new revenue stream by reselling training programs.
- Provide additional value to existing compliance clients.
- Scale effortlessly without increasing your workload.
Grow your consulting business with training-as-a-service
Whether you’re a solo consultant or run a compliance agency, the Company Training Academy helps you provide more value to your clients while reducing overhead.
Create training accounts for clients of any size – from just a few, to thousands of users, with flexible pricing for every client size.
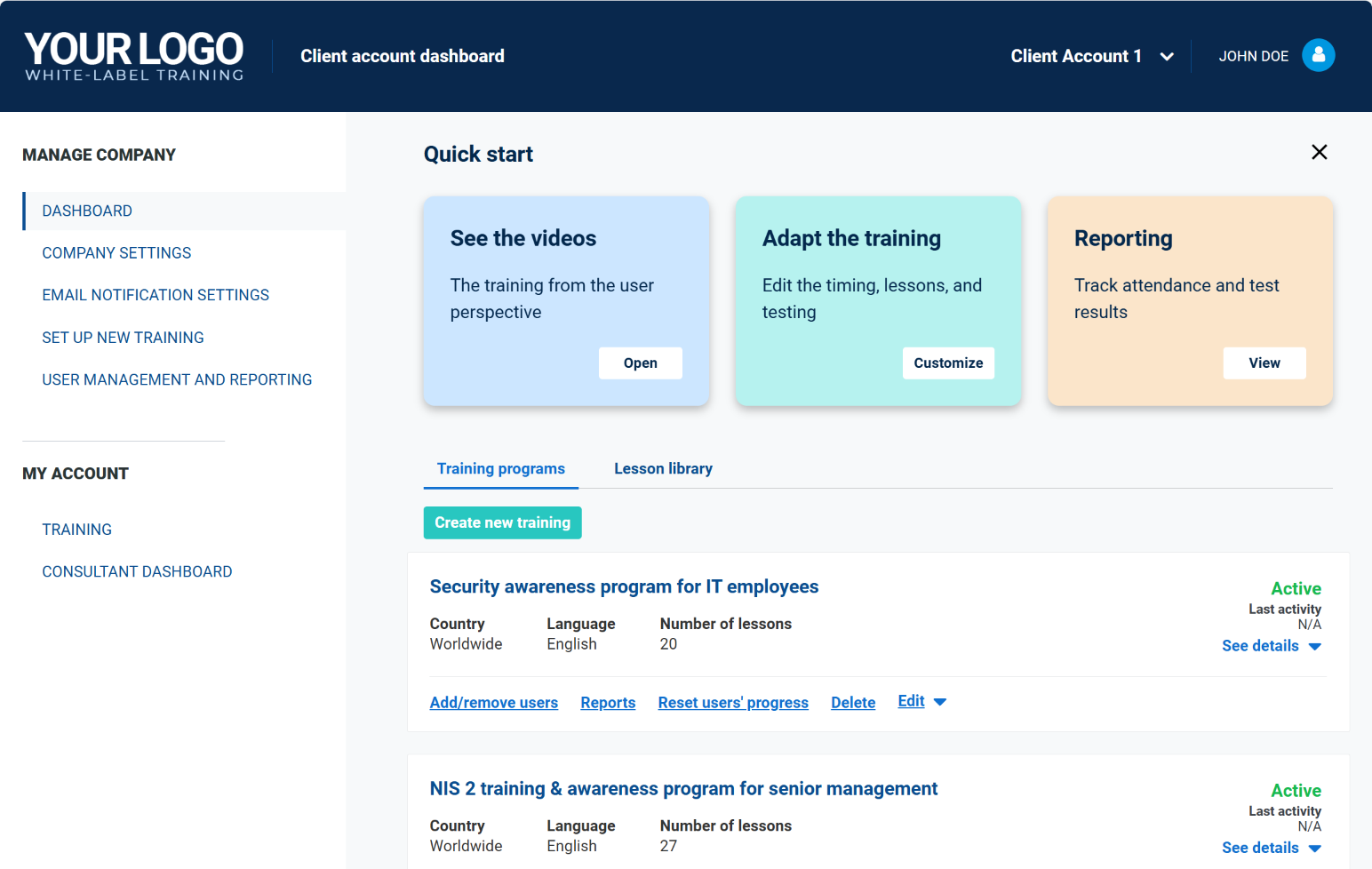
Features designed for your consulting business
Tailored for consultants, this hassle-free training-as-a-service platform includes all the essential features to grow your business and support your clients.
For your own company
For consultants
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Company Training Academy?
The Company Training Academy is a learning management system (LMS) that enables you to configure various training and awareness programs for your entire workforce for, e.g., NIS2, DORA, ISO 27001, GDPR, ISO 42001, security awareness, etc.
How can I get a free trial as a consultant?
As a consultant, you'll receive a free trial account after a short call with our support team. We'll walk you through the platform, answer your questions, and then provide full access so you can test all consultant-specific features during the 14-day free trial before committing.
Can I manage multiple client accounts with one login?
Yes — you’ll have a central dashboard to manage all your clients.
Can I use my own branding?
Yes — our white-label feature lets you offer a fully branded experience.
Do I need separate subscriptions for each client?
You’ll be billed for each client account separately, based on the number of users. You manage all accounts from your dashboard.
Can I resell this as part of my services?
Absolutely. You can set your own pricing for your clients and bundle this with your other offerings.
Can I transfer ownership of a client account to the client?
Yes. If requested, we can transfer full ownership of a specific training account to your client — including all user data, training records, and settings. Just reach out to our support team when you're ready.
Can I upload our own materials to the Company Training Academy?
Yes. You can upload your company’s own training materials and create lessons from them. Supported formats include documents (PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLSX, etc.), videos (YouTube, Vimeo), and text-based lessons you can create directly in the editor.
What forms of payment do you accept?
We accept payment via any major credit or debit card; for a larger number of users, you can pay via wire transfer from your bank account.
How long does it take to set up a training program on a client account?
Opening a client account takes less than a minute. The wizard will then guide you through the process of setting up your first training and awareness program, which usually takes 5–10 minutes.
Which standards and regulations are covered in the Company Training Academy videos?
Currently, the videos cover NIS2, DORA, ISO 27001, GDPR, ISO 42001, and cybersecurity awareness training.
We’re working on adding videos for other standards and regulations.
Are videos available in languages other than English?
Besides English, we currently have videos in German, French, Italian, Dutch, Spanish, Portuguese, and Croatian. We are working on adding more languages at the moment; please contact us to learn about available languages.
Is there a time limit for attending the training?
No, your users can spend as much time as they like attending the lessons, as long as your subscription is active.
What will the users need to access the lessons?
Your users can access the lessons using PC, Mac, or mobile devices, using any major browser (e.g., Chrome, Mozilla, Edge, Safari); a broadband Internet link will also be needed.
What is the format of the training, and how long does it take?
The lessons are a combination of video lectures, quizzes, and test questions. The average time needed per lesson is between 5 and 10 minutes. You can configure your training program to include only a couple of lessons, or several dozen lessons.
What prior knowledge is needed to attend the training?
None. The lessons are created in such a way that a beginner can easily understand them. They are very easy to follow for any type of employees — senior or mid-level management, non-IT employees, tech people, etc.
There are so many videos — how will I find what is the most appropriate for us?
The Company Training Academy will suggest the most appropriate videos based on the framework you’re interested in (e.g., NIS2), and based on your audience (e.g., senior management).
Further, you can filter all the videos in the Library by country, language, relevant clauses and articles of the framework, and other criteria.
Schedule a Demo
Want our expert to walk you through the product? Schedule a short call. We respond quickly.
