Many companies would like to enhance their quality management, but they are still unsure whether to start with ISO 9001 or GMP, since both of these are focused on quality. Read this article to find out how to decide which one to choose.
ISO 9001 and GMP are quality frameworks for businesses offering products or services. ISO 9001 is a Quality Management System standard, while GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices. Both are equally important, but ISO 9001 applies to any industry, and GMP is only for manufacturing food, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices.
What are ISO 9001 and GMP?
ISO 9001 is the International Organization for Standardization’s Quality Management System (QMS) standard. It is a globally recognized framework applicable to virtually any industry, and it allows voluntary certification by an external party. According to ISO, over 1.2 million organizations are certified in more than 170 countries. This standard focuses on the general principles of quality management, such as top management commitment, customer focus, process approach, and continual improvement.
GMP regulations are mandatory in the EU for cosmetic products and are highly recommended by many other countries, such as the United States. In the United States, GMP is enforced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP), which cover a broader range of industries such as cosmetics, food, medical devices, and prescription drugs. Similarly, the FDA has established CGMPs for food and dietary supplements to ensure the safety of these products. Therefore, while GMP regulations are enforced in many countries, they may be mandatory in some and highly recommended in others.
GMP rules ensure that products consistently meet high quality standards, are suitable for their intended use, and comply with marketing authorization or clinical trial authorization. Unlike ISO standards, which are voluntary, GMP is legally binding, and compliance is enforced by national or supervising authorities. GMP is essential to guarantee product safety, consistency, and effectiveness, as it helps maintain rigorous quality control and manufacturing standards within the pharmaceutical, medical device, food, and cosmetic industries.
What are the key differences between ISO 9001 and GMP?
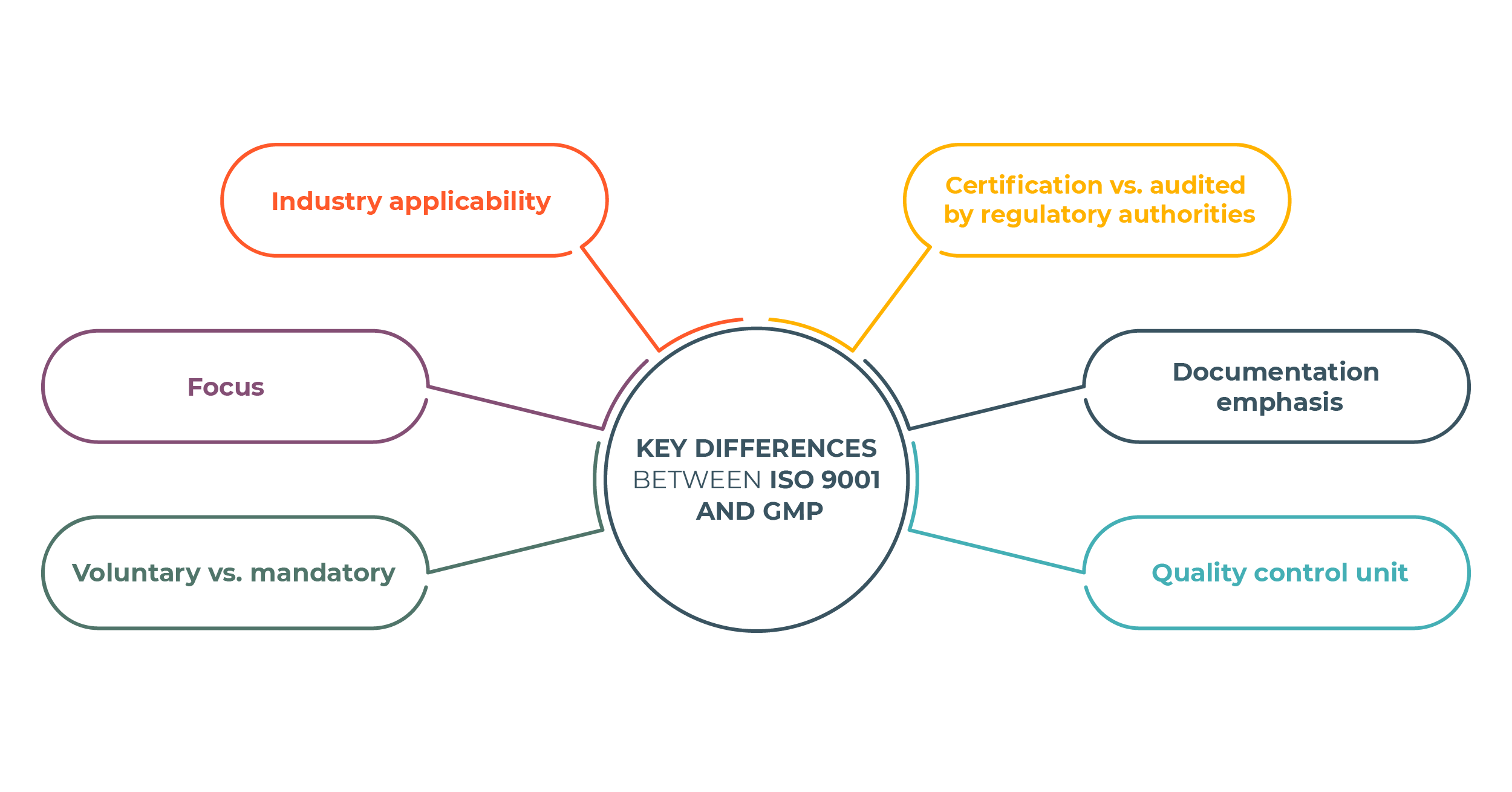
ISO 9001 and GMP are Quality Management Systems widely used in the manufacturing industry, but they have some key differences. Here are the main differences between ISO 9001 and GMP:
- Industry Applicability: The most significant difference is the industries these standards apply to. ISO 9001 applies to all organizations, including manufacturing, services, healthcare, etc. In contrast, GMP applies exclusively to the pharmaceutical, medical devices, cosmetics, and food industries, where product safety and efficacy are essential. It guarantees that products are manufactured, tested, and controlled following rigorous guidelines.
- Focus: GMP focuses on manufacturing to ensure the safety, identity, strength, quality, and purity of pharmaceuticals and food. It safeguards consumers from potential harm. At the same time, ISO 9001 is more concerned with the company’s overall management and Quality Management System, with a strong customer focus – meeting customer requirements, exceeding customer expectations, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Voluntary vs. Mandatory: ISO 9001 certification is voluntary, with organizations adopting the standard for competitive advantage and customer satisfaction. GMP compliance is mandatory and regulated by government agencies.
- Certification vs. Audited by Regulatory Authorities: Organizations can achieve ISO 9001 certification through third-party audits conducted by accredited certification bodies chosen by the organization. GMP compliance is verified through inspections and audits conducted by regulatory authorities, and non-compliance can result in regulatory actions.
- Documentation Emphasis: Both standards require documentation, but GMP’s documentation is particularly stringent, given the critical nature of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, cosmetics, and food products.
- Quality Control Unit: GMP regulations require establishing a quality control unit responsible for product approval and rejection. In contrast, ISO 9001 does not explicitly prescribe the creation of a quality control unit vested with the authority to approve or reject products. Instead, ISO 9001 encourages organizations to define roles and responsibilities in quality management. If quality control units exist, the standard does not dictate their specific composition and authority.
What are the similarities between ISO 9001 and GMP?
ISO 9001 and GMP converge on several key issues in quality management. Both standards prioritize consistent quality and operational excellence. ISO 9001 and GMP emphasize process optimization and documented procedures to uphold established standards. Both advocate a process-oriented approach, requiring ongoing evaluation for enhanced quality outcomes.
Customer-centricity and regulatory adherence are shared principles, underscoring the alignment of both standards in meeting customer needs and complying with industry regulations for sustained quality assurance. This convergence highlights their mutual emphasis on stringent processes, documentation, and continuous improvement to ensure consistent quality across different sectors and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
How can ISO 9001 complement GMP?
Even though ISO 9001 and GMP each have a somewhat different focus, implementing them together is a smart idea.
The process approach and customer focus outlined in ISO 9001 can significantly complement GMP by enhancing the Quality Management System within regulated industries.
ISO 9001’s process approach, when applied to non-GMP areas (such as administration, human resources, or sales), allows for mapping and managing interconnected workflows and activities. By identifying, analyzing, and optimizing these processes, efficiency can be improved, redundancies reduced, and potential bottlenecks identified.
ISO 9001 places a strong emphasis on understanding and meeting customer requirements. Integrating customer-focused principles into GMP encourages organizations to consider regulatory compliance and the end-user’s needs and expectations. By aligning manufacturing processes with customer requirements, GMP can prioritize product quality, efficacy, and safety in a way that directly meets or exceeds customer expectations. It can lead to developing compliant products that resonate with end-users, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Integrating ISO 9001 into GMP enhances operational efficiency, risk management, product quality, and customer satisfaction in regulated industries while providing a stronger compliance framework. This ensures GMP practices meet regulations and deliver quality products that meet customer needs.
Start implementing quality management practices with our ISO 9001 Premium Documentation Toolkit, which provides step-by-step guidance for full ISO 9001 compliance.

 Carlos Pereira da Cruz
Carlos Pereira da Cruz