Tracey Evans
Tracey Evans
May 3, 2021
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) according to the ISO 27001 standard.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ISMS according to ISO 27001.
Train your key people about ISO 27001 requirements and provide cybersecurity awareness training to all of your employees.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance and training products for critical infrastructure organizations for the European Union’s Network and Information Systems cybersecurity directive.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Company-wide training program for employees and senior management to comply with Article 20 of the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Compliance and training products for financial entities for the European Union’s DORA regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the DORA regulation.
Company-wide cybersecurity and resilience training program for all employees, to train them and raise awareness about ICT risk management.
Accredited courses for individuals and DORA professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance and training products for personal data protection according to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU GDPR privacy regulation.
Train your key people about GDPR requirements to ensure awareness of data protection principles, privacy rights, and regulatory compliance.
Accredited courses for individuals and privacy professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 9001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a QMS according to ISO 9001.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) according to the ISO 14001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an EMS according to ISO 14001.
Accredited courses for individuals and environmental professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 14001 and the EMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation and training products for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) according to the ISO 45001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an OHSMS according to ISO 45001.
Accredited courses for individuals and health & safety professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation and training products for medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 13485 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a medical device QMS according to ISO 13485.
Accredited courses for individuals and medical device professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance products for the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU MDR.
Implementation products for Information Technology Service Management Systems (ITSMS) according to the ISO 20000 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ITSMS according to ISO 20000.
Implementation products for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) according to the ISO 22301 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a BCMS according to ISO 22301.
Implementation products for testing and calibration laboratories according to the ISO 17025 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement ISO 17025 in a laboratory.
Implementation products for automotive Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the IATF 16949 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an automotive QMS according to IATF 16949.
Implementation products for aerospace Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the AS9100 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an aerospace QMS according to AS9100.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for consultancies.
Handle multiple ISO 27001 projects by automating repetitive tasks during ISMS implementation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement various standards and regulations for your clients.
Grow your business by organizing cybersecurity and compliance training for your clients under your own brand using Advisera’s learning management system platform.
Accredited Lead Auditor and Lead Implementer courses for ISO standards and DORA, and an advanced course to help consultants grow their business.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Find new clients, potential partners, and collaborators and meet a community of like-minded professionals locally and globally.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for the IT industry.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity), and DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance, training, and knowledge products for essential and important organizations.
Documentation to comply with NIS 2 (cybersecurity), GDPR (privacy), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), and ISO 22301 (business continuity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for manufacturing companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for transportation & distribution companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for schools, universities, and other educational organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for telecoms.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for banks, insurance companies, and other financial organizations.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for local, regional, and national government entities.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for hospitals and other health organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the medical device industry.
Documentation to comply with MDR and ISO 13485 (medical device), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the aerospace industry.
Documentation to comply with AS9100 (aerospace), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the automotive industry.
Documentation to comply with IATF 16949 (automotive), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for laboratories.
Documentation to comply with ISO 17025 (testing and calibration laboratories), ISO 9001 (quality), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
 Tracey Evans
Tracey Evans
Once a testing or calibration laboratory has implemented ISO/IEC 17025:2017 as part of its management system, it moves into a maintenance and monitoring phase. This is a not a dormant, but rather a dynamic phase of operation, where processes are monitored and trends are reviewed. During this “live” operational phase, it is time to review the system.
This article will help you gain a better understanding of what management review (MR) means, as well as its importance and value. It will provide some practical guidance on how to go about the management review and how to structure your documents to meet ISO 17025:2017 clause 8.9 requirements.
Management review is neither an audit nor a report-back discussion. It is not about reporting measurements, but evaluating to what extent the management system fulfills its functions and goals. Management review is a strategic planning opportunity. The purpose of a management review is for top management and personnel involved in the decision-making processes to systematically evaluate the overall performance of the laboratory and its Quality Management System.
To learn more about the maintenance of the ISO 17025 management system, read this: Maintaining and improving quality management in laboratories according to ISO 17025:2017.
Organizations and stakeholders (including the accreditation body) need to be assured of the continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the laboratory’s management system, along with its stated policies and objectives. When shortcomings are identified through management review, provisions can be made for necessary changes and required resources.
Efficiency should also be evaluated to ensure best use of allocated resources. There are, therefore, four key parameters that are considered during management review in ISO/IEC 17025:
To clarify a misconception about management reviews, note that the review doesn’t have to be a singular annual meeting covering all requirements. The management review can be conducted over a number of meetings with previously written agendas, where partial inputs may even be evaluated via email or other collaborative platforms at different levels within the laboratory. Responsibility is usually assigned to the top laboratory manager, who will conduct a final review with the gathered information and contributions. This can be done in a review meeting.
To meet the intent of the review, typically, at least one review of the entire management system should be performed each year. The output of the review is to set goals and objectives for the forthcoming period, so it is good practice to align the review period with the organization’s financial year, parent company strategy sessions, and the laboratory’s accreditation assessments. It makes sense to complete the review in a timely manner for budget input. Processes or annual programs, such as auditing, should in turn be aligned to the MR period, meaning that the audit program should be completed before the MR meeting.
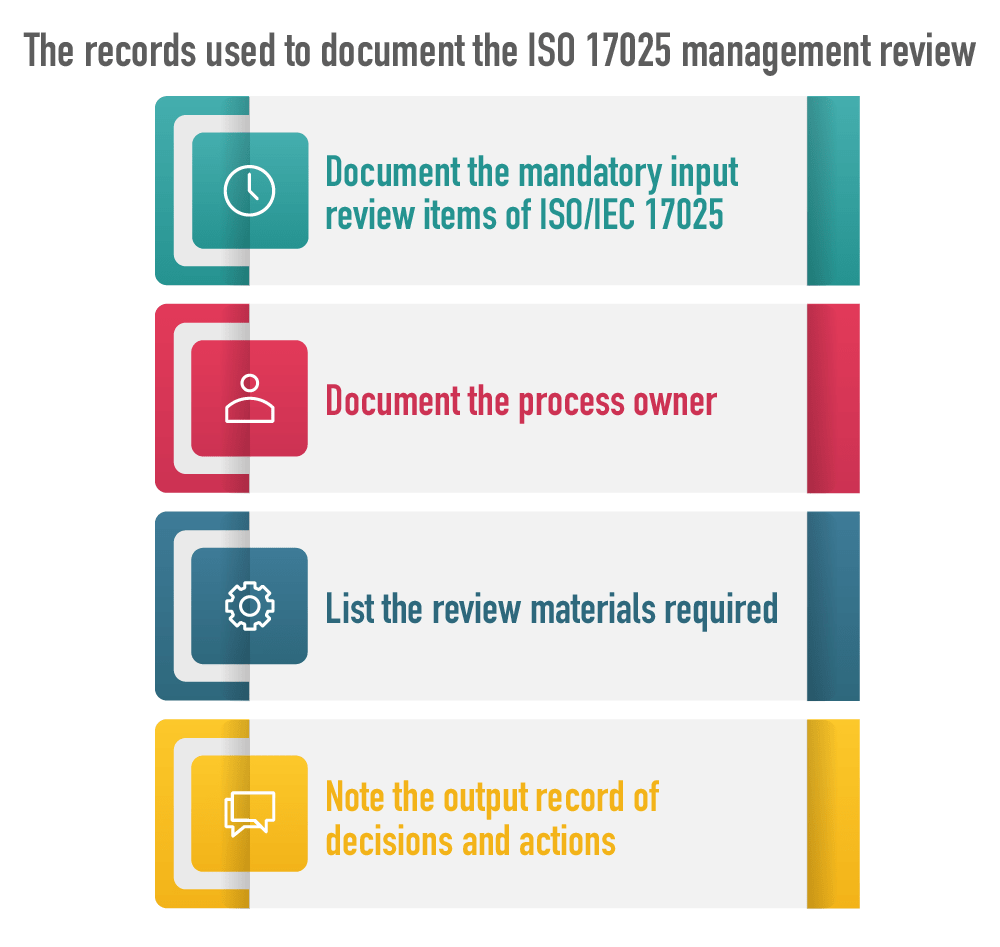
Since the quality goal of the ISO 17025 management review is the careful analysis and evaluation of the management system, a well-designed Management Review Record should be used as the core document of the activity. It can be used for planning, recording the inputs, and recording and monitoring progress of agreed actions. There is no mandatory requirement for documents such as an agenda or minutes, so the Review Record can be used for both purposes.
The record is used to document the following:
For example, for the input “Results of risk identification,” the outputs could be the following:
It is important that all personnel are informed about the results of management reviews, the conclusions, and new quality aims. The information and communication can even be via email, as long as personnel have access to the latest management review record, and follow-up is ongoing and engaging through discussions and meetings.
Some tips for effective follow-up, monitoring, and closing actions are:
A final tip: Do not forget to ask all involved personnel for feedback to evaluate the success of the completed management review process, as an input to improve the next one!
To comply with all ISO 17025 requirements, use this helpful ISO 17025 Documentation Toolkit that provides all documents for laboratories.


You may unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy notice.