Updated: November 8, 2023.
If you’re working with ISO 27001, you’ve surely came across the term “Information Security Management System” or ISMS. Pretty vague term, isn’t it?
In the following article, we will give you an overview of the main aspects of an ISMS, and show you how you can implement it to get the most out of its benefits.
ISO 27001 basically describes how to develop the Information Security Management System (ISMS). An ISMS describes how to manage security through technological, organizational, people, and physical security aspects.
An ISMS describes how security is managed through various policies and procedures, and its aim is to protect sensitive information handled by a company.
Why should you implement an ISMS?
An ISMS aims to protect and safeguard data, and its implementation provides an ideal framework for ensuring that information is always proper for use, and that it is not disclosed to unintended people. It’s also a way to make sure that, if an incident occurs, the negative impact will be minimal.
This is important because information is a key element of organizations’ routines, which is why the standard requires that it be kept safe in a systematic way, by satisfying security requirements from various stakeholders. Additionally, due to its importance, information can attract the attention of malicious parties (e.g., dissatisfied employees, industrial spies, information thieves, etc.) who want to profit from it, and who don’t care about who will be harmed. This is why companies also need to prevent and/or handle the actions of such malicious parties.
What are the benefits of an ISMS?
Besides the direct result of taking care of information, by implementing an ISMS, a company can experience several positive effects. There are at least six benefits:
- Centralized security management. An ISMS provides a common point for information security management, ensuring that all initiatives are aligned and resources are optimized.
- Increased resilience. An ISMS minimizes the occurrence of compromised information and the impact of any incidents that occur as a result. In this way, an Information Security Management System allows businesses to quickly recover normal operation status.
- Decreased compliance effort. An ISMS enables better monitoring and understanding of how to fulfill the requirements of laws, regulations, and contractual requirements related to information security.
- Reduced costs. By allocating resources where they are more effective, and by reducing losses and expenses related to security breaches, an ISMS helps to keep information security costs to a minimum.
- Increased customer confidence. When companies are less affected by compromised information, an ISMS contributes to the establishment of longer partnerships, and sometimes even recommendations that result in new leads, users, or buyers.
- Improvement of internal culture. An ISMS works to improve people’s understanding of the importance of protecting information, and raises their security awareness.
How does ISO 27001 apply to an ISMS?
As a leading information security management standard, ISO 27001 puts forth clear requirements for an ISMS. As an international standard, ISO 27001 makes it easier for companies to ensure that they are implementing all the necessary elements.
One of the main contributions of ISO 27001 to an ISMS is that it offers the flexibility to decide which security elements to implement — according to ISO 27001, information security controls should be selected based on the results of risk assessment and the applicable requirements of interested parties. This means that ISO 27001 allows flexibility when managing the ISMS, so that companies can decide what kind of security is needed based on their specific risk profile and the customers they serve.
How to implement an Information Security Management System according to ISO 27001
So, what does ISMS implementation need to look like according to ISO 27001?
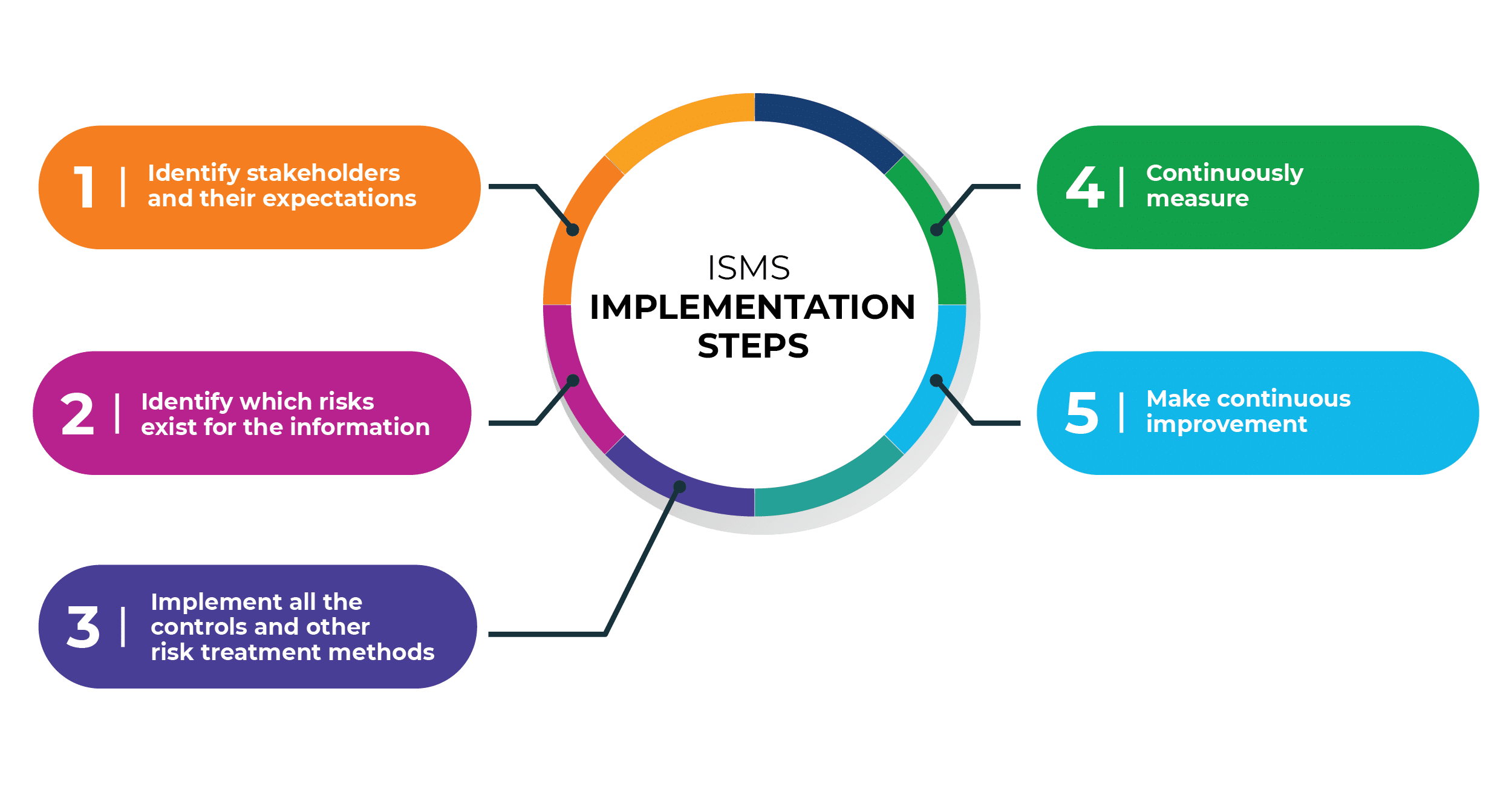
To simplify, these general steps are needed to implement ISMS according to ISO 27001:
- Define stakeholders and their security requirements.
- Find out which security risks exist for the company.
- Implement all required security controls.
- Measure if controls perform as expected.
- Continuously improve how the ISMS works.
When defining how to implement an Information Security Management System, the required rules can be written down in the form of policies, procedures, and other types of documents, or you can implement them in the form of established processes and technologies that are not documented. ISO 27001 defines which documents are required, i.e., which must exist at a minimum.
An ISMS example: Implementing several controls for an asset
Let’s take a laptop as an example — you can decrease the risk to the data on this laptop by applying several different controls, for example:
- Write a procedure that states that you cannot leave the laptop in the car.
- Protect your laptop with a password, so if it gets stolen it will be more difficult for someone to access your information.
- Encrypt your disk — this is an even higher level of information protection.
- Ask your employees to sign a statement obligating them to pay for any damage that occurs in the event such an incident happens.
- Train and make your employees aware that there are security risks if they leave their laptops in their cars.
Now, protecting one laptop might sound simple, but the problem grows when you have hundreds of laptops, dozens of servers, a multitude of software, many employees, etc. With so much data and users, it would be extremely difficult to manage all controls (safeguards) without some kind of a system — and that system is the ISMS. An Information Security Management System is a framework that explains how to manage such a complex security system.
Risks related to an Information Security Management System
As with any other system, an ISMS is only as good as the people who manage and operate it, so the main risks related to an ISMS are:
- Lack of understanding of the importance of the ISMS when managing security. This leads to implementing security controls unsystematically, which means implementing controls that are not needed, or not implementing controls that are needed, leading to overall chaos when trying to manage all those controls.
- Not considering the ISMS as a part of business strategy. Information security needs to support the main strategy of the company — e.g., if a company wants to expand into a new market, the top management needs to determine how the ISMS can help them with this strategic objective.
- Unclear objectives. Information security needs to be measurable, so that it is easy to show its value to the top management. If the objectives are vague (e.g., “We want to be more secure”), then it would be very difficult to measure the progress — instead, they need to be measurable, e.g., “Increase the number of customers by 5% because of ISO 27001 (ISMS) certification.”
Why ISMS?
Generally speaking, people either do not understand what an ISMS is, or do not appreciate its value.
However, by implementing an ISMS according to ISO 27001, companies get a very tangible way to manage security. And on top of that, they can start using security not only for managing risks, but also to improve their overall business.
To see all the necessary tasks for ISMS implementation and maintenance, and to learn how to comply with ISO 27001 with less bureaucracy, sign up for a free trial of Conformio, the leading ISO 27001 compliance software.

 Dejan Kosutic
Dejan Kosutic