After nine years, ISO 27001, the world’s leading information security standard, has been updated — on October 25, 2022, the new ISO/IEC 27001:2022 was published. Even though this revision brings only moderate changes, it is important to study them closely — let’s go through all the changes and see how this 2022 revision compares to the old 2013 revision of ISO 27001.
- The main part of ISO 27001, i.e., clauses 4 to 10, has changed only slightly.
- The changes in Annex A security controls are moderate.
- The number of controls has decreased from 114 to 93.
- The controls are placed into 4 sections, instead of the previous 14.
- There are 11 new controls, while none of the controls were deleted, and many controls were merged.
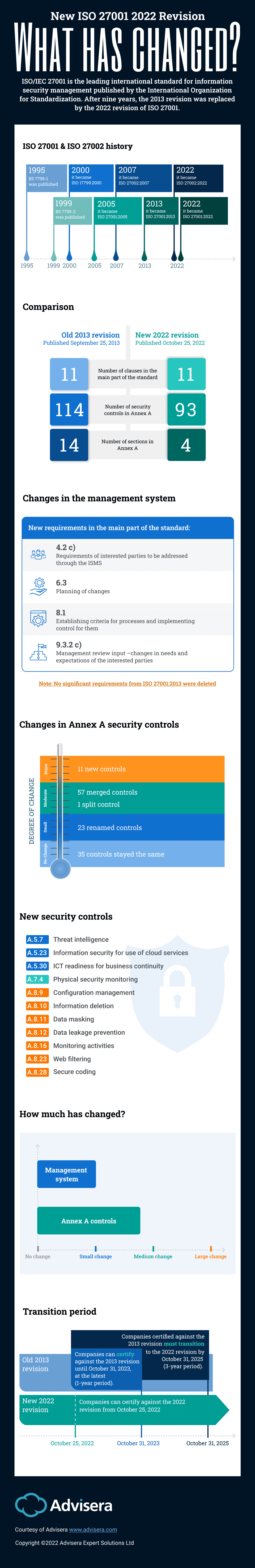
ISO 27001 & ISO 27002 history
The first version of ISO 27001 was published way back in 1999 under the name of BS 7799-2, and it has gone through several changes since then.
ISO 27001 should not be confused with ISO 27002 — the former one is the main standard against which you can certify your company, while the latter one is the supporting standard that provides guidelines on the implementation of security controls. The most important difference is that ISO 27002 is not mandatory for ISO 27001 certification, and a company cannot get certified against ISO 27002.
ISO 27002 was first published in 1995 under the name of BS 7799-1, and in February 2022 the ISO 27002:2022 revision was published with the new structure of 93 controls — this exact same structure of controls was adopted by ISO 27001:2022, as explained below.
Comparison
Overall, when compared to the ISO 27001:2013 standard, the changes in the 2022 revision are small to moderate. The main part of the standard remains with 11 clauses, and the changes in this part of the standard are small (see below).
At first glance, Annex A has changed a lot — the number of controls has dropped from 114 to 93, and it is organized into only four sections versus the 14 sections in the 2013 revision. However, after a closer look, it becomes obvious that the changes in Annex A are only moderate — see the explanation below.
Changes in the management system
The text of the mandatory clauses 4 through 10 has changed only slightly, mainly to align with ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and other ISO management standards, and with Annex SL.
Here’s a brief overview of the changes in ISO 27001:2022:
- In clause 4.2 (Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties), item (c) was added requiring an analysis of which of the interested party requirements must be addressed through the ISMS.
- In clause 4.4 (Information security management system), a phrase was added requiring planning for processes and their interactions as part of the ISMS.
- In clause 5.3 (Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities), a phrase was added to clarify that communication of roles is done internally within the organization.
- In clause 6.2 (Information security objectives and planning to achieve them), item (d) was added that requires objectives to be monitored.
- Clause 6.3 (Planning of changes) was added, requiring that any change in the ISMS needs to be done in a planned manner.
- In clause 7.4 (Communication), item (e) was deleted, which required setting up processes for communication.
- In clause 8.1 (Operational planning and control), new requirements were added for establishing criteria for security processes, and for implementing processes according to those criteria. In the same clause, the requirement to implement plans for achieving objectives was deleted.
- In clause 9.3 (Management review), the new item 9.3.2 c) was added that clarifies that inputs from interested parties need to be about their needs and expectations, and relevant to the ISMS.
- In clause 10 (Improvement), the subclauses have changed places, so the first one is Continual improvement (10.1), and the second one is Nonconformity and corrective action (10.2), while the text of those clauses has not changed.
Changes in Annex A security controls
In reality, the changes in Annex A are only moderate because most of the controls have either stayed the same (35 of them) or have only been renamed (23). Another 57 controls were merged, which has reduced the number of controls, but the requirements within those controls remained almost the same. Finally, one control was split into two separate controls, while the requirements stayed the same. To see how the controls have changed, download this free white paper: Overview of new security controls in ISO 27002:2022.
There are 11 new controls, which were needed because of the trends in IT and security — you can see the details here: Detailed explanation of 11 new security controls in ISO 27001:2022.
Tip: You can use this ISO 27001:2013 to ISO 27001:2022 Conversion Tool to find out how the controls from the old revision of the standard map with the new ones.
Is ISO 27001:2013 obsolete?
As of the writing of this article, ISO 27001:2013 is not yet obsolete. The three-year grace period for companies to transition to ISO 27001:2022 began in October 2022.
Transition period
According to the document “Transition requirements for ISO/IEC 27001:2022” from the International Accreditation Forum, for companies that are already certified against ISO 27001:2013, the transition to the ISO 27001 latest version needs to be completed by October 31, 2025.
Certification bodies were required to start certifying companies against ISO 27001:2022 by October 31, 2023, at the latest, but I’m sure most of them began with this new revision much sooner.
Tip: If you already implemented the old 2013 revision of the standard, and want to make a transition to the 2022 revision of ISO 27001, schedule a free consultation with our ISO 27001 expert.
How much has changed?
To summarize, changes in the main part of the standard are only small and can be done rather quickly, with only slight changes in the documentation and processes. Changes in the Annex A controls are moderate and can be mostly dealt with by adding the new controls to the existing documentation.
After nine (long) years of waiting for this new revision, some security professionals were expecting the changes to be more extensive, but I believe that companies that are already certified against the 2013 revision will be relieved that the work to be done is not that big after all.
If you want to start implementing the 2022 revision of ISO 27001, sign up for a free trial of Conformio, the leading ISO 27001 compliance software.

 Dejan Kosutic
Dejan Kosutic