Term ‘residual risk’ is mandatory in the risk management process according to ISO 27001, but is unfortunately very often used without appreciating the real meaning of the concept.
Residual risk is the risk remaining after risk treatment. After you identify the risks and mitigate the risks you find unacceptable (i.e. treat them), you won’t completely eliminate all the risks because it is simply not possible – therefore, some risks will remain at a certain level, and this is what residual risks are.
The point is, the organization needs to know exactly whether the planned treatment is enough or not.
Residual risks are usually assessed in the same way as you perform the initial risk assessment – you use the same methodology, the same assessment scales, etc. What is different is that you need to take into account the influence of controls (and other mitigation methods), so the likelihood of an incident is usually decreased and sometimes even the impact is smaller.
For more information about the risk management process read ISO 27001 Risk Assessment, Treatment, & Management: The Complete Guide.
How is it related to acceptable level of risk?
I mentioned that the purpose of residual risks is to find out whether the planned treatment is sufficient – the question is, how would you know what is sufficient? This is where the concept of acceptable level of risks comes into play – it is nothing else but deciding how much ‘risk appetite’ an organization has, or in other words whether the management thinks it is fine for a company to operate in a high-risk environment where it is much more likely that something will happen, or the management wants a higher level of security involving a lower level of risk.
Both approaches are allowed in ISO 27001 – each organization has to decide what is appropriate for its circumstances (and for its budget). The former approach is probably better for high-growth startup companies, while the letter is usually pursued by financial organizations.
Residual risk management
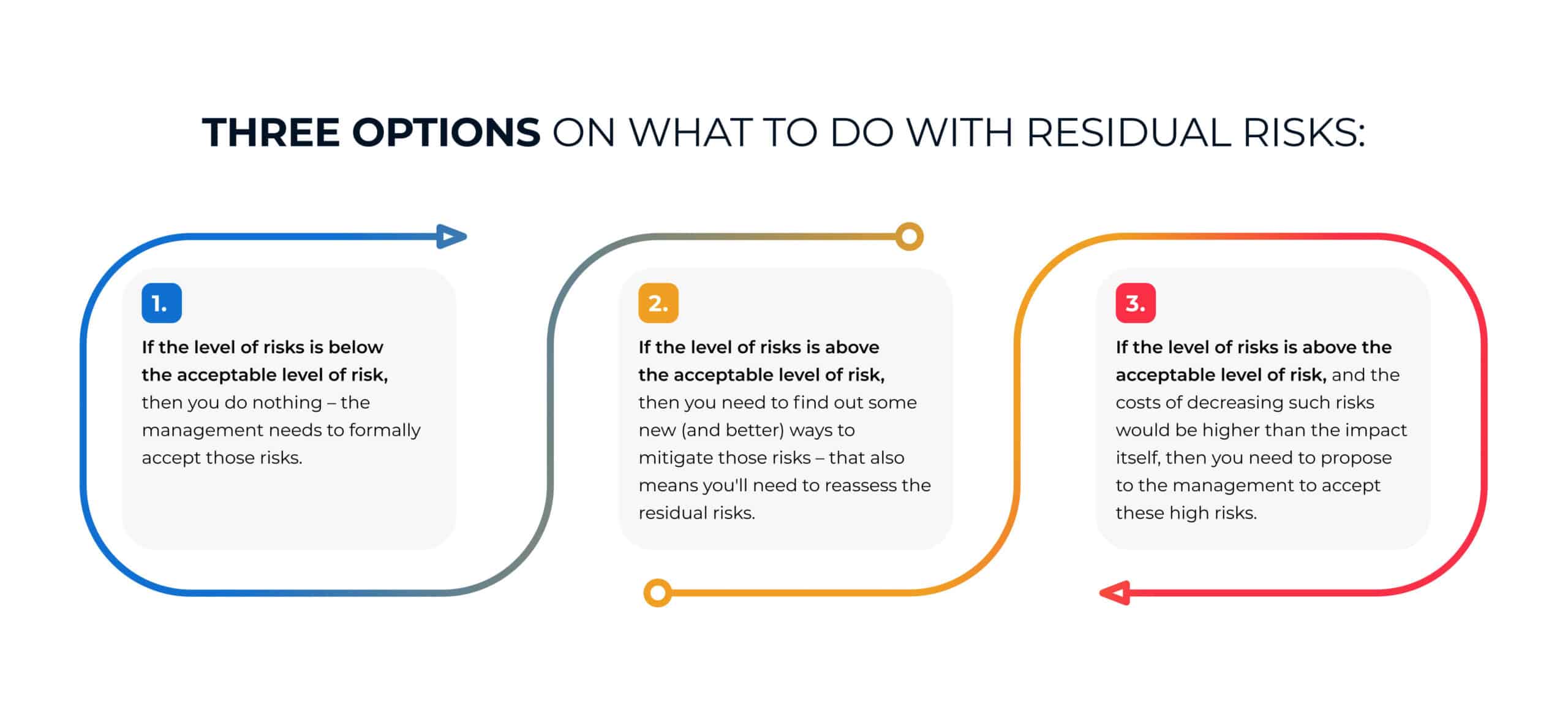
Once you find out what residual risks are, what do you do with them? Basically, you have these three options:
- If the level of risks is below the acceptable level of risk, then you do nothing – the management needs to formally accept those risks.
- If the level of risks is above the acceptable level of risk, then you need to find out some new (and better) ways to mitigate those risks – that also means you’ll need to reassess the residual risks.
- If the level of risks is above the acceptable level of risk, and the costs of decreasing such risks would be higher than the impact itself, then you need to propose to the management to accept these high risks.
Such a systematic way ensures that management is involved in reaching the most important decisions, and that nothing is overlooked.
So the point is – top management needs to know which risks their company will face even after various mitigation methods have been applied. After all, top management is not only responsible for the bottom line of the company, but also for its viability.
To see how to use the ISO 27001 risk register with catalogs of assets, threats, and vulnerabilities, and get automated suggestions on how they are related, sign up for a free trial of Conformio, the leading ISO 27001 compliance software.

 Dejan Kosutic
Dejan Kosutic