Rhand Leal
Rhand Leal
January 30, 2022
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) according to the ISO 27001 standard.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ISMS according to ISO 27001.
Train your key people about ISO 27001 requirements and provide cybersecurity awareness training to all of your employees.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance and training products for critical infrastructure organizations for the European Union’s Network and Information Systems cybersecurity directive.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Company-wide training program for employees and senior management to comply with Article 20 of the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Compliance and training products for financial entities for the European Union’s DORA regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the DORA regulation.
Company-wide cybersecurity and resilience training program for all employees, to train them and raise awareness about ICT risk management.
Accredited courses for individuals and DORA professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance and training products for personal data protection according to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU GDPR privacy regulation.
Train your key people about GDPR requirements to ensure awareness of data protection principles, privacy rights, and regulatory compliance.
Accredited courses for individuals and privacy professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 9001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a QMS according to ISO 9001.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) according to the ISO 14001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an EMS according to ISO 14001.
Accredited courses for individuals and environmental professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 14001 and the EMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation and training products for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) according to the ISO 45001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an OHSMS according to ISO 45001.
Accredited courses for individuals and health & safety professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation and training products for medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 13485 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a medical device QMS according to ISO 13485.
Accredited courses for individuals and medical device professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance products for the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU MDR.
Implementation products for Information Technology Service Management Systems (ITSMS) according to the ISO 20000 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ITSMS according to ISO 20000.
Implementation products for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) according to the ISO 22301 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a BCMS according to ISO 22301.
Implementation products for testing and calibration laboratories according to the ISO 17025 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement ISO 17025 in a laboratory.
Implementation products for automotive Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the IATF 16949 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an automotive QMS according to IATF 16949.
Implementation products for aerospace Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the AS9100 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an aerospace QMS according to AS9100.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for consultancies.
Handle multiple ISO 27001 projects by automating repetitive tasks during ISMS implementation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement various standards and regulations for your clients.
Grow your business by organizing cybersecurity and compliance training for your clients under your own brand using Advisera’s learning management system platform.
Accredited Lead Auditor and Lead Implementer courses for ISO standards and DORA, and an advanced course to help consultants grow their business.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Find new clients, potential partners, and collaborators and meet a community of like-minded professionals locally and globally.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for the IT industry.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity), and DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance, training, and knowledge products for essential and important organizations.
Documentation to comply with NIS 2 (cybersecurity), GDPR (privacy), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), and ISO 22301 (business continuity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for manufacturing companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for transportation & distribution companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for schools, universities, and other educational organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for telecoms.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for banks, insurance companies, and other financial organizations.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for local, regional, and national government entities.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for hospitals and other health organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the medical device industry.
Documentation to comply with MDR and ISO 13485 (medical device), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the aerospace industry.
Documentation to comply with AS9100 (aerospace), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the automotive industry.
Documentation to comply with IATF 16949 (automotive), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for laboratories.
Documentation to comply with ISO 17025 (testing and calibration laboratories), ISO 9001 (quality), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
 Rhand Leal
Rhand Leal
Updated: December 12, 2022, according to ISO 27001 2022 revision.
It’s been nine years since the last revision of ISO/IEC 27002 (in 2013), and although ISO 27001:2013 was confirmed in 2019 (i.e., no changes in the Information Security Management System standard were required) – ISO 27002 definitely needed improvement to fulfill its role as guidance for implementation of ISO 27001 Annex A controls.
The new 2022 revision of ISO 27002 was published on February 15, 2022, and, in this article, I’ll present the main changes when compared to ISO 27002:2013 – these are not only about controls, but also how to organize and use them.
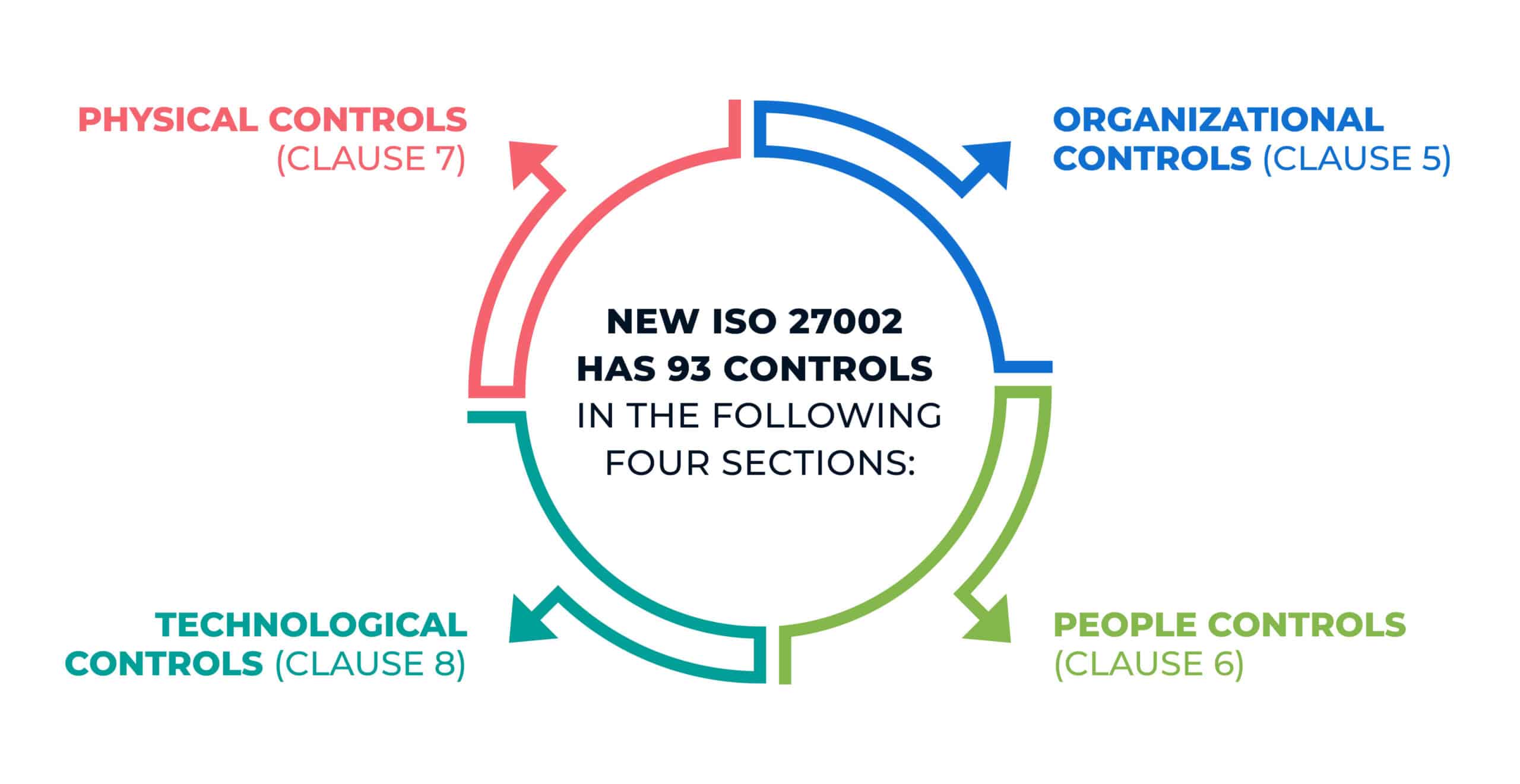
From the previous 14 sections, ISO 27002:2022 now has only four sections, along with two annexes:
This new structure makes it easier to understand the applicability of the controls in a high-level sense, as well as the designation of responsibilities.
This new version has reduced the number of controls from 114 to 93. Technological advancements, and an improvement to the understanding of how to apply security practices, seem to be the reasons for the change in number of controls.
The controls in the new version of ISO 27002 have two new elements in their structure:
These added elements make it easier to find information to better understand how to sort and justify the use of a control.
Additionally, in the new ISO 27002, one level of subtitle was eliminated. As a comparative example, access control was previously “9 Access control – 9.1 Business requirements of access control – 9.1.1 Access control policy,” whereas it is now “5 Organizational controls – 5.15 Access control.”
In my opinion, this is the change that brings the most value for this new version, because it provides a standardized way to sort and filter controls against different views to address the needs of different groups.
Attributes options for each control are as follows:
These attributes will ease the integration of ISO 27002:2022 controls with other similar security frameworks, like NIST Risk Management Framework.
Here are the 11 controls that are new:
To learn more about these new controls and their requirements, read the article Detailed explanation of 11 new security controls in ISO 27001:2022.
23 controls have had their names changed for the sake of making them easier to understand. For example:
These changes help keep the focus on the information security aspects of business processes and activities, reducing the effort for implementing and maintaining the Information Security Management System.
To see a full list of controls in the new ISO 27002, and to learn which controls were renamed and merged when compared to ISO 27002:2013, download this free white paper: Overview of new security controls in ISO 27002:2022.
Although the number of controls has been reduced, no controls were excluded in this new version, only merged for the sake of better understanding.
57 controls have been merged into 24 controls. For example:
In my understanding, these merges were considered either because related controls are natural steps of a bigger process, or because more efficient security could be achieved by considering them in a single control.
There is only one control that was split: 18.2.3 Technical compliance review was split into 5.36 Conformance with policies, rules and standards for information security and 8.8 Management of technical vulnerabilities.
35 controls remained the same, only changing their control number.
If you already have your Information Security Management System implemented according to ISO 27001, you don’t have to worry too much for now – no matter which changes the new ISO 27002 revision has brought, there will be a transition period of three years for certified companies to align with these new controls, and that period starts on October 31, 2022.
Once these new controls become part of ISO 27001 Annex A, you will need to follow these steps:
Since this change in the standard involves 11 new controls, this alignment in risk treatment and documentation will be the biggest job that’s ahead of you, although it probably will not require a big change in technological and process areas.
And this is where the new ISO 27002 will bring the most value – during the transition period you will have plenty of refreshed best practices to choose from, as well as a new set of attributes to use to make controls selection easier and more effective. And because ISO 27002 is quite detailed, and you still have the freedom to choose only the appropriate stuff for your organization, it will definitely help you make this transition easier.
To automate your compliance with ISO 27001 security controls, sign up for a free trial of Conformio, the leading ISO 27001 compliance software.

Rhand Leal has more than 15 years of experience in information security, and for six years he continuously maintained а certified Information Security Management System based on ISO 27001.
Rhand holds an MBA in Business Management from Fundação Getúlio Vargas. Among his certifications are ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, ISO 9001 Lead Auditor, Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), and others. He is a member of the ISACA Brasília Chapter.
You may unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy notice.