We live in a world where businesses face mounting pressure from regulators, investors, and customers to prove their commitment to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Failing to act means not just reputational damage, but also financial and regulatory consequences. This is the reality organizations are grappling with today as the call for credible climate action grows louder. How can companies rise to this challenge, align with global best practices, and demonstrate transparency in their climate strategies?
ISO 14064, the global standard revolutionizing GHG management, provides a robust framework to measure, reduce, and verify emissions while enhancing transparency.
ISO 14064: A brief overview
Established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2006, ISO 14064 is a globally recognized standard offering a clear, structured approach to managing, measuring, and reporting GHG emissions. Designed to cut through the complexities of climate-related accountability, ISO 14064 equips businesses, governments, and projects with the tools to track their carbon footprints, reduce emissions effectively, and meet regulatory and voluntary commitments. Whether you’re navigating new climate disclosure rules or aiming to lead in sustainability, ISO 14064 provides the framework to get there.
Key features of ISO 14064
ISO 14064 offers comprehensive guidelines to help organizations quantify, monitor, report, and verify their GHG emissions and removals. It is designed to be used globally, providing organizations, policymakers, and stakeholders with a reliable and consistent method for addressing climate change issues.
ISO 14064 has a three-part structure:
- Part 1 focuses on creating and managing GHG inventories at the organizational level. It establishes principles and requirements for identifying emission sources, setting boundaries, collecting data, and reporting emissions transparently and consistently.
- Part 2 offers specific guidelines for quantifying, monitoring, and reporting GHG emission reductions and removal enhancements at the project level. This supports initiatives like carbon offset programs.
- Part 3 standardizes the process for validating and verifying GHG assertions to ensure credibility and accuracy. This part is crucial for independent audits or internal verifications.
ISO 14064 highlights the importance of transparency, accuracy, completeness, consistency, and relevance in ensuring robust and comparable GHG data. This standard is not linked to any specific national or international climate policy, which makes it versatile and widely applicable, regardless of a country’s climate commitments. Furthermore, ISO 14064 aligns with other frameworks, such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, by establishing minimum standards for adhering to best practices.
Applications of ISO 14064
ISO 14064 can be used for various purposes:
- For businesses: Provides a pathway to manage emissions inventories cost effectively, ensuring transparency and comparability with other organizations.
- For governments: Acts as a foundation for voluntary or regulatory climate programs, focusing efforts on achieving policy objectives while adhering to international best practices.
- For verification: Facilitates independent verification, ensuring that reported data meets interested parties’ needs for reliability and decision making.
By adopting ISO 14064, organizations show their commitment to tackling climate change, enhancing stakeholders’ trust, and establishing themselves as leaders in sustainability. It serves as a key tool for entities looking to effectively navigate the global challenge of reducing GHG emissions.
Why is ISO 14064 becoming more important?
ISO 14064 is becoming increasingly significant due to growing regulatory, market, and societal pressures to address climate change and reduce carbon footprints.
Regulatory requirements
In Europe, initiatives like the European Green Deal, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), and the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) emphasize the need for rigorous greenhouse gas accounting and reporting. Similarly, in the United States, policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) underscore the importance of transparency in carbon management.
Learn more about the importance of regulatory compliance in these articles: How to achieve regulatory compliance in ISO 14001 and Environmental Compliance — Why it Matters and How To Obtain It.
Market demands
Investors, customers, and stakeholders call for detailed and credible sustainability disclosures, particularly regarding decarbonization efforts. ISO 14064 provides a standardized approach, enhancing trust in GHG inventories and aligning with global frameworks like the GHG Protocol.
Voluntary commitments
A growing number of companies are setting net-zero and science-based targets, which require robust systems for measuring and verifying emissions and removals.
Supply chain pressure
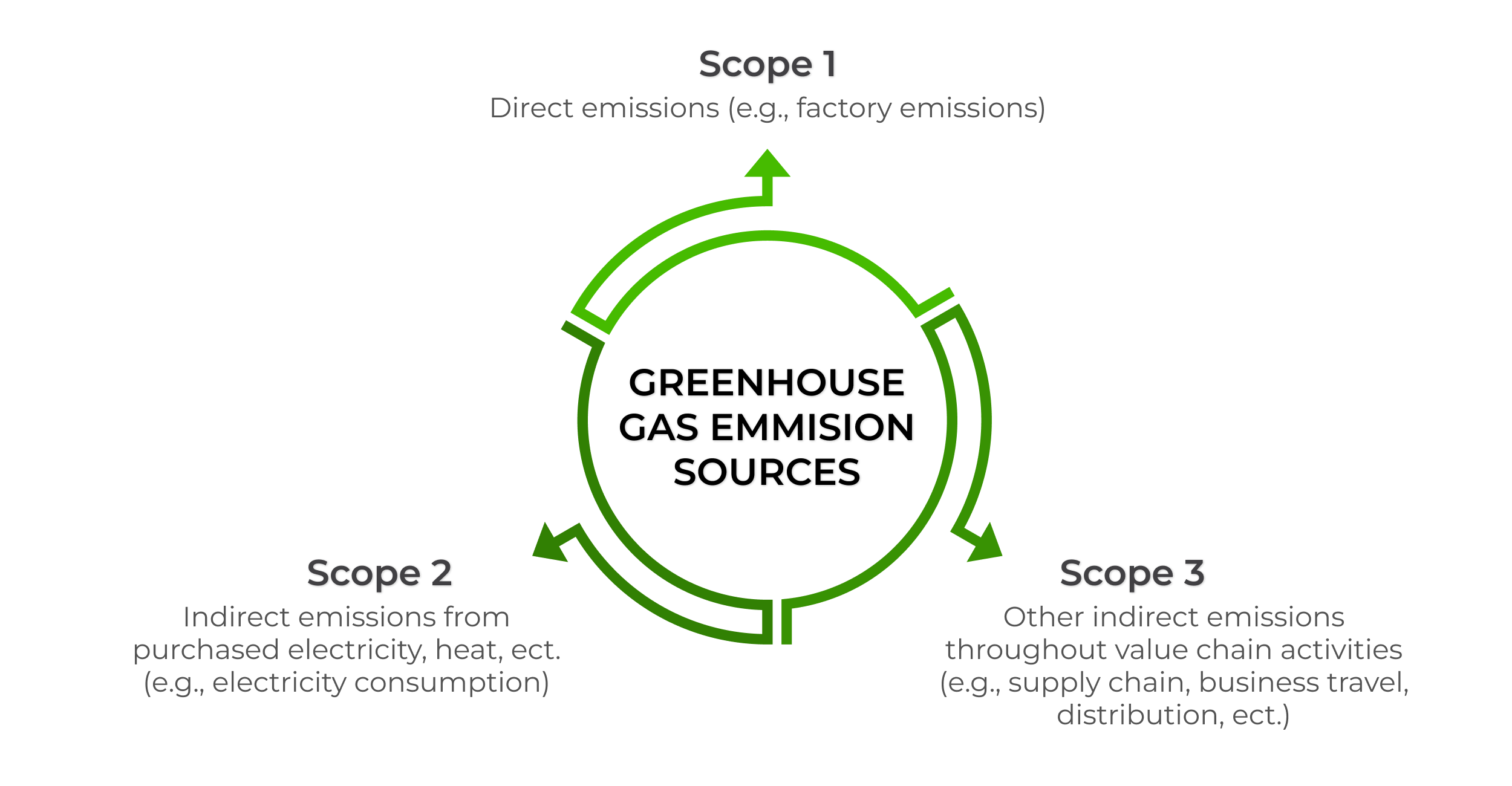
Organizations face increasing demands from stakeholders to disclose and reduce Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. This often necessitates ISO 14064-aligned reporting to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Note: Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions categorize greenhouse gas emissions based on their source. Scope 1 covers direct emissions from owned or controlled sources, like company vehicles or facilities. Scope 2 includes indirect emissions from purchased energy, such as electricity. Scope 3 accounts for all other indirect emissions across the value chain, like supplier activities, business travel, and product use.
What is the purpose of each part of ISO 14064?
ISO 14064 is a critical standard for managing greenhouse gas emissions, structured into three distinct parts, each serving a specific purpose.
Part 1: Quantification and Reporting at the Organization Level
The purpose of this section is to establish principles and requirements for organizations to measure, manage, and report their greenhouse gas emissions and removals. It guides organizations in defining their boundaries, both organizational and operational, and in creating a comprehensive and accurate inventory of direct and indirect emissions. It also emphasizes the use of consistent methodologies for quantification and encourages clear, transparent, and verifiable reporting of findings. This section is fundamental for organizations seeking to monitor their carbon footprints and ensure accountability in their climate-related initiatives.
Part 2: Quantification, Monitoring, and Reporting at the Project Level
This section focuses on specific projects designed to reduce GHG emissions or enhance removals. It provides guidance on quantifying baseline emissions and comparing them with reductions achieved by the project. Additionally, it covers monitoring the ongoing impact of initiatives such as carbon capture or renewable energy projects and reporting findings to demonstrate measurable contributions to GHG mitigation. Examples include renewable energy projects and afforestation programs. This section is particularly relevant for entities involved in carbon offset projects.
Part 3: Verification and Validation of GHG Statements
This section outlines a standardized approach to verifying and validating GHG emissions data and reports. It ensures the accuracy and credibility of reported GHG emissions, reductions, or removals and supports independent validation of the assumptions and methodologies used. Transparency is emphasized for stakeholders, including regulators, investors, and the public. This section is crucial for third-party audits and for compliance with emissions-trading schemes and other regulatory frameworks.
Steps to implement ISO 14064
Defining boundaries. Under ISO 14064, organizations must clearly determine their GHG reporting boundaries, deciding which facilities, operations, and activities fall within their direct control or significant influence.
Measuring emissions. Organizations identify and quantify greenhouse gas sources across all relevant scopes, following standardized methodologies and emission factors in line with ISO 14064.
Reporting findings. ISO 14064 emphasizes transparent documentation of the methodology, assumptions, and calculations used to measure emissions. Clear and consistent reporting of GHG data builds credibility and allows for meaningful comparison over time or against industry benchmarks.
Validation and verification. An independent validation or verification process ensures the accuracy and reliability of reported GHG information under ISO 14064. This step provides external assurance for stakeholders, reinforcing accountability and confidence in the organization’s emissions data.
How can ISO 14064 and ISO 14001 work together?
ISO 14064 and ISO 14001 are complementary standards that can be integrated to enhance an organization’s environmental and climate change management systems. ISO 14001 provides a framework for managing overall environmental performance, while ISO 14064 focuses specifically on greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating both standards, organizations can ensure comprehensive environmental and climate action strategies.
The GHG inventory and measurement data from ISO 14064 can be used to inform the environmental aspects and objectives of ISO 14001, thereby improving environmental decision making and performance tracking. Furthermore, ISO 14001 emphasizes a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which can incorporate GHG emissions management from ISO 14064 as a critical component of environmental goals.
Organizations that adopt both standards can demonstrate compliance with legal requirements and voluntary commitments, ensuring credibility and transparency. Integrating these standards also streamlines internal audits, stakeholder communications, and verification processes, reducing duplication of effort and enhancing operational efficiency.
Together, ISO 14064 and ISO 14001 provide a cohesive and systematic approach to addressing environmental sustainability and climate change. This integration equips organizations with a robust toolset to manage their overall environmental impact and specific GHG emissions while meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
To comply with all ISO 14001 requirements, use this helpful ISO 14001 Premium Documentation Toolkit that provides all EMS documents.

 Carlos Pereira da Cruz
Carlos Pereira da Cruz