Mark Hammar
Mark Hammar
May 27, 2019
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) according to the ISO 27001 standard.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ISMS according to ISO 27001.
Train your key people about ISO 27001 requirements and provide cybersecurity awareness training to all of your employees.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance and training products for critical infrastructure organizations for the European Union’s Network and Information Systems cybersecurity directive.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Company-wide training program for employees and senior management to comply with Article 20 of the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Compliance and training products for financial entities for the European Union’s DORA regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the DORA regulation.
Company-wide cybersecurity and resilience training program for all employees, to train them and raise awareness about ICT risk management.
Accredited courses for individuals and DORA professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance and training products for personal data protection according to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU GDPR privacy regulation.
Train your key people about GDPR requirements to ensure awareness of data protection principles, privacy rights, and regulatory compliance.
Accredited courses for individuals and privacy professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 9001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a QMS according to ISO 9001.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) according to the ISO 14001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an EMS according to ISO 14001.
Accredited courses for individuals and environmental professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 14001 and the EMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation and training products for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) according to the ISO 45001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an OHSMS according to ISO 45001.
Accredited courses for individuals and health & safety professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation and training products for medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 13485 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a medical device QMS according to ISO 13485.
Accredited courses for individuals and medical device professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance products for the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU MDR.
Implementation products for Information Technology Service Management Systems (ITSMS) according to the ISO 20000 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ITSMS according to ISO 20000.
Implementation products for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) according to the ISO 22301 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a BCMS according to ISO 22301.
Implementation products for testing and calibration laboratories according to the ISO 17025 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement ISO 17025 in a laboratory.
Implementation products for automotive Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the IATF 16949 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an automotive QMS according to IATF 16949.
Implementation products for aerospace Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the AS9100 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an aerospace QMS according to AS9100.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for consultancies.
Handle multiple ISO 27001 projects by automating repetitive tasks during ISMS implementation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement various standards and regulations for your clients.
Grow your business by organizing cybersecurity and compliance training for your clients under your own brand using Advisera’s learning management system platform.
Accredited DORA, ISO 27001, 9001, 14001, 45001, and 13485 courses for professionals who want the highest-quality training and recognized certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Find new clients, potential partners, and collaborators and meet a community of like-minded professionals locally and globally.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for the IT industry.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity), and DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance, training, and knowledge products for essential and important organizations.
Documentation to comply with NIS 2 (cybersecurity), GDPR (privacy), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), and ISO 22301 (business continuity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for manufacturing companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for transportation & distribution companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for schools, universities, and other educational organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for telecoms.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for banks, insurance companies, and other financial organizations.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for local, regional, and national government entities.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for hospitals and other health organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the medical device industry.
Documentation to comply with MDR and ISO 13485 (medical device), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the aerospace industry.
Documentation to comply with AS9100 (aerospace), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the automotive industry.
Documentation to comply with IATF 16949 (automotive), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for laboratories.
Documentation to comply with ISO 17025 (testing and calibration laboratories), ISO 9001 (quality), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
 Mark Hammar
Mark Hammar
Many companies use a SWOT analysis in their business planning, and this can be a helpful tool to use in the Occupational Health & Safety Management System (OHSMS) as well. ISO 45001:2018 requires a company to identify top-level issues, risks, and opportunities, which is exactly what the SWOT analysis does. This is why ISO 45001 can use SWOT analysis as a very useful tool to address the above-mentioned requirements of the standard.
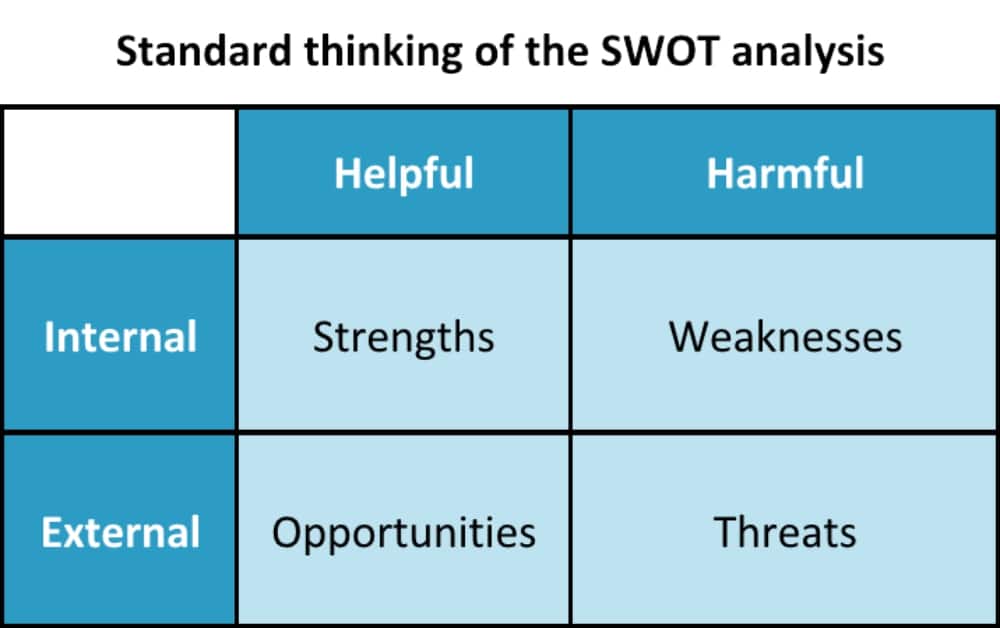
SWOT is an acronym that stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The SWOT analysis is a systematic approach for an organization to identify the internal strengths and weaknesses of the organization, as well as the external opportunities and threats that affect the organization. As a strategic planning approach, this tool is used to perceive the competitive position of a company, which allows you to identify items that can be addressed to fix current problems and develop future potential.
Typically, the process is used as a brainstorming session where top management considers where they are doing well and where they can improve. In general, if an issue is internal and helpful, it is a strength of the organization; however, if it is internal and harmful, it is a weakness. Likewise, if an issue is external and potentially helpful, it is an opportunity, and if it is external and potentially harmful, it is a threat. These are then listed on a chart, such as the one shown below, for assessment.
Once known, the issues are assessed. For internal strengths, is there some way that the company can use this to their advantage? And for weaknesses, does the company need to take action to make sure these weaknesses do not harm the organization? With external opportunities, does the company want to take action to try to capture these positive chances, including taking some risk to capture them? And for threats, does the company need to take action to prevent these negative risks from occurring, dependent on the potential consequences?
For more about risk, read the article What to include in risk management methodology according to ISO 45001:2018.
There are three clauses in ISO 45001:2018 that can be addressed by using a SWOT analysis technique. The first is clause 4.1, Understanding the organization and its context, which requires you to determine the internal and external issues that are relevant to the OHSMS. The second is clause 6.1.2.2, Assessment of OH&S risks and other risks to the OH&S management system, which asks you to assess other OH&S management system risks (called “threats” in the SWOT analysis). Finally, clause 6.1.2.3, Assessment of OH&S opportunities and other opportunities for the OH&S management system, requires you to assess what you will do about opportunities for improving OH&S performance. While SWOT analysis is not used to assess risks and opportunities, it can be used to identify the risks and opportunities that need to be assessed.
So, if you approach the SWOT analysis with a focus on occupational health & safety, you can identify the internal and external issues that affect your OHSMS and the ability to meet your OH&S performance goals. You can also identify the risks and opportunities that need to be considered for the future of your OHSMS. The SWOT analysis is a tool that can be used to identify and categorize these different considerations for your OHSMS.
An example of the SWOT analysis used for OH&S could include the following identified elements: Strength – The company has a strong employee attitude towards maintaining a safe workplace; Weakness – The company is growing, so many new employees are being added and OH&S training is delayed; Opportunity – A supplier has identified a new chemical that is less hazardous to employee health, and that may be acceptable for use in our cleaning process; Threat – Changing customer requirements indicate that a current process chemical may need to be replaced with a more hazardous chemical.
Once identified, you can then determine what actions you will take to address each issue, risk, or opportunity. Note that this does not mean that actions need to be taken for everything. If you assess an opportunity and determine that you do not want to pursue it, then you do not need to. Likewise, if the actions to address a risk exceed the potential consequences of the risk happening, you can also choose to do nothing about a risk. The SWOT analysis is a tool to identify, not a mandate to control.
One thing to remember is that these clauses of the ISO 45001 standard are common to all of the ISO standards, so the SWOT analysis can be used to identify internal and external issues, opportunities, and risks for all of the different management systems you choose to implement. If you also implement ISO 9001:2015, the SWOT analysis can be used with a focus on providing goods and services. If you have an Environmental Management System using ISO 14001:2015, then your SWOT analysis can focus on environmental performance.
The SWOT analysis is a tool that can be very helpful, but it is up to you to determine if it is the right tool for your organization. The ISO standards do not tell you how to meet the requirements, so if a SWOT analysis helps your company to improve, then use it to the best of your ability.
To implement ISO 45001 easily and efficiently, use our ISO 45001 Premium Documentation Toolkit that provides step-by-step guidance and all documents for full ISO 45001 compliance.


You may unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy notice.