Strahinja Stojanovic
Strahinja Stojanovic
November 9, 2017
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) according to the ISO 27001 standard.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ISMS according to ISO 27001.
Train your key people about ISO 27001 requirements and provide cybersecurity awareness training to all of your employees.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance and training products for critical infrastructure organizations for the European Union’s Network and Information Systems cybersecurity directive.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Company-wide training program for employees and senior management to comply with Article 20 of the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Compliance and training products for financial entities for the European Union’s DORA regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the DORA regulation.
Company-wide cybersecurity and resilience training program for all employees, to train them and raise awareness about ICT risk management.
Accredited courses for individuals and DORA professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance and training products for personal data protection according to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU GDPR privacy regulation.
Train your key people about GDPR requirements to ensure awareness of data protection principles, privacy rights, and regulatory compliance.
Accredited courses for individuals and privacy professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 9001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a QMS according to ISO 9001.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) according to the ISO 14001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an EMS according to ISO 14001.
Accredited courses for individuals and environmental professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 14001 and the EMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation and training products for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) according to the ISO 45001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an OHSMS according to ISO 45001.
Accredited courses for individuals and health & safety professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation and training products for medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 13485 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a medical device QMS according to ISO 13485.
Accredited courses for individuals and medical device professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance products for the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU MDR.
Implementation products for Information Technology Service Management Systems (ITSMS) according to the ISO 20000 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ITSMS according to ISO 20000.
Implementation products for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) according to the ISO 22301 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a BCMS according to ISO 22301.
Implementation products for testing and calibration laboratories according to the ISO 17025 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement ISO 17025 in a laboratory.
Implementation products for automotive Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the IATF 16949 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an automotive QMS according to IATF 16949.
Implementation products for aerospace Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the AS9100 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an aerospace QMS according to AS9100.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for consultancies.
Handle multiple ISO 27001 projects by automating repetitive tasks during ISMS implementation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement various standards and regulations for your clients.
Grow your business by organizing cybersecurity and compliance training for your clients under your own brand using Advisera’s learning management system platform.
Accredited Lead Auditor and Implementer courses for DORA and ISO standards and advanced courses to help consultants grow their business, increase recurring revenue, and stand out from bigger competitors.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Find new clients, potential partners, and collaborators and meet a community of like-minded professionals locally and globally.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for the IT industry.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity), and DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance, training, and knowledge products for essential and important organizations.
Documentation to comply with NIS 2 (cybersecurity), GDPR (privacy), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), and ISO 22301 (business continuity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for manufacturing companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for transportation & distribution companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for schools, universities, and other educational organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for telecoms.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for banks, insurance companies, and other financial organizations.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
Documentation to comply with DORA (cybersecurity for financial sector), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for local, regional, and national government entities.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for hospitals and other health organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the medical device industry.
Documentation to comply with MDR and ISO 13485 (medical device), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity) and GDPR (privacy).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the aerospace industry.
Documentation to comply with AS9100 (aerospace), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the automotive industry.
Documentation to comply with IATF 16949 (automotive), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for laboratories.
Documentation to comply with ISO 17025 (testing and calibration laboratories), ISO 9001 (quality), and NIS 2 (critical infrastructure cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
 Strahinja Stojanovic
Strahinja Stojanovic
Updated: September 30, 2023
Many companies see management review as an unpleasant necessity for maintaining compliance with ISO 13485. If used properly, however, this is far from the truth. Regardless of how you organize your ISO 13485 management review, either through routinely scheduled meetings or a more continuous review process, the act of reviewing the available data can be one of the biggest drivers of improvement in the Quality Management System (QMS). Learn more about the ISO 13485 management review requirements in this article.
Requirement 5.6 of the ISO 13485 standard covers the management review process. This involves evaluating the effectiveness and suitability of the Quality Management System, identifying opportunities for improvement, and making changes to the system as needed. The ISO 13485 management review process is a critical component of maintaining compliance with the standard and driving QMS improvement.
The purpose of the ISO 13485 management review is to evaluate the effectiveness and suitability of an organization’s Quality Management System and identify opportunities for improvement. This process involves reviewing mandatory inputs such as customer feedback, audits, and regulatory reporting, and making changes to the Quality Management System as needed. By properly conducting an ISO 13485 management review, organizations can use the available data to drive QMS improvement and achieve greater customer satisfaction.
ISO 9001 doesn’t require documented procedures for management review and, in general, tends to require fewer mandatory procedures with its latest version (for more information, see: Infographic: ISO 9001:2015 vs. 2008 revision – What has changed?). ISO 13485, however, is aligned more with 21 CFR 820.20(c), which says: “Management … shall review … according to established procedures ….” For more information, see: Differences and similarities between FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485.
The management review needs to be conducted at planned intervals to ensure the continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of a QMS based on ISO 13485. It also needs to include the assessment of opportunities for improvement and changes in the QMS. Finally, the records of the management review need to be kept as evidence of compliance.
Although other inputs could be added as desired by the company, ISO 13485 has a minimum list of 12 inputs that top management need to review to assess the health of the QMS. Without holding meetings, there are several smaller reviews that need to happen in order to determine if the QMS is adequate for your needs.
Feedback and compliance handling. Generally, this is a review of data and metrics directly correlated with the customer experience (e.g., customer complaint metrics, customer survey results), product performance, and pre-existing, product-specific continuous improvement projects.
Reporting to regulatory authorities. The organization needs to review its process for reporting to the regulatory authorities, as well as the reasons for reporting.
Audits. Does the company management representative review the audit reports and ensure that they are included in the audit planning for the year? If so, then you have someone in management who is reviewing the results of audits and how they are improving the management system. Any audit reports, if they include this review information, are not only records of the audits, but also records of the management review.
Monitoring and measurement of processes. Does your company keep metrics of the main processes, sometimes called key performance indicators (KPIs), which are used to judge the adequacy of the processes? If these KPIs are in place, reviewed by the top management, and used to make resource decisions on improvements to the processes, then management review is taking place.
Corrective and preventive action. The top management doesn’t have to review every single corrective action. Instead, in order to define actions for improvement, they should be informed of the effectiveness of the actions taken and trends in nonconformity occurrences.
Follow-up from previous management review. This requirement is accomplished if the previously mentioned actions receive follow-up to ensure they were implemented. The best way to ensure this is to review the minutes from the last ISO 13485 management review meeting. The most important thing is to ensure that the records show this follow-up review.
Changes that could affect the QMS. The organization needs to track outside influences that could affect the system, such as the new version of the standard. In addition, reviews regarding internal information will address changes within the organization, such as recommendations for improvement or internal audits.
Recommendations for improvement. Some recommendations for improvement, such as those coming out of the internal audit, can be addressed as part of that system as stated above. Other recommendations, such as those from an employee suggestion system, will often be tracked on a log that can be reviewed.
Applicable new or revised regulatory requirements. The top management needs to be updated on changes in regulations that could impact the QMS and/or the business.
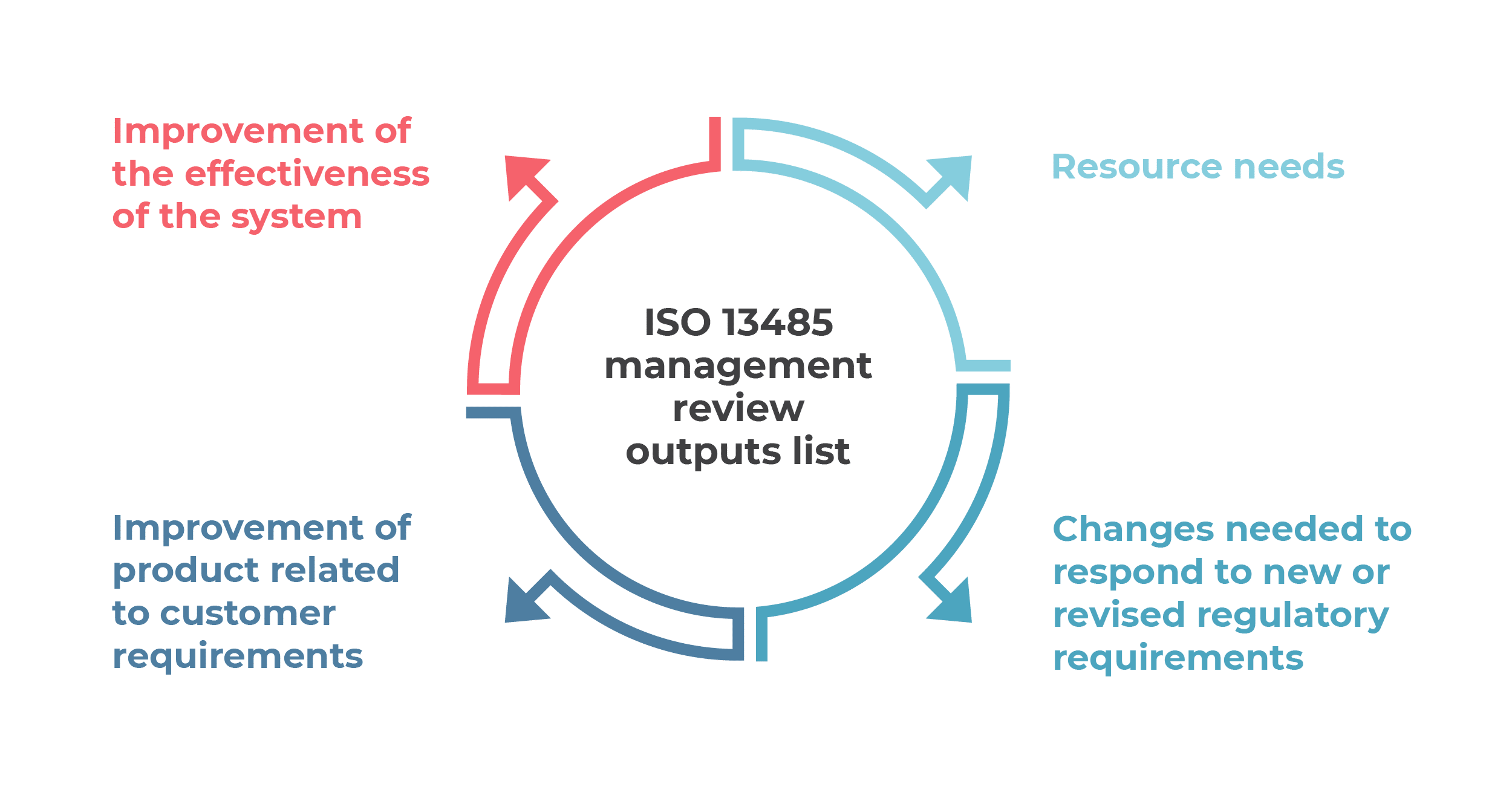
The headings below are the mandatory outputs of management review, and records of the above queries need to be maintained to show that management review successfully addressed them and identified the outputs for the QMS.
Improvement of the effectiveness of the system. Improvement is the big driver of the ISO 13485 QMS, and it can be the largest benefit for a company that implements it. Process improvement is measured by savings in time, money, and resources, and this can be fed back into greater profits or driving the system to improve even further.
Improvement of product related to customer requirements. Again, by improving the product or service to make it more effectively meet the requirements of the customer, you can have greater customer satisfaction. More customers will return for your product or service, or tell their friends about it to drive in new customers.
Resource needs. Using management review to try to focus on improvements can help drive savings in costs and resources by making sure they are applied in the right place from the start. Using data to drive decisions helps to ensure that those decisions are accurate.
Changes needed to respond to new or revised regulatory requirements. The top management needs to define the actions necessary to achieve compliance with regulatory requirements and keep the organization current with laws and regulations.
When all of these elements are included in the ISO 13485 management review meeting minutes, they provides an overview of all the activities that the organization undertook within the defined period.
Once you go through the ISO 13485 management review, you will see that this process highlights all the areas to make sure the top management are monitoring and controlling the necessary resources to keep the company functioning. Instead of being a burden, management review should become one of the main elements of QMS improvement. Management review is all about reviewing the available data to confirm that adequate resources are present to ensure customer satisfaction and improve the QMS and the product.
To implement ISO 13485 easily and efficiently, use our ISO 13485 Documentation Toolkit that provides step-by-step guidance and all documents for full ISO 13485 compliance.

Strahinja Stojanovic is certified as a lead auditor for the ISO 13485, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OHSAS 18001 standards by RABQSA. He participated in the implementation of these standards in more than 100 SMEs, through the creation of documentation and performing in-house training for maintaining management systems, internal audits, and management reviews.


You may unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy notice.